This is a fixed-text formatted version of a Jupyter notebook
- Try online
- You can contribute with your own notebooks in this GitHub repository.
- Source files: simulate_3d.ipynb | simulate_3d.py
3D simulation and fitting¶
This tutorial shows how to do a 3D map-based simulation and fit.
For a tutorial on how to do a 3D map analyse of existing data, see the analysis_3d tutorial.
This can be useful to do a performance / sensitivity study, or to evaluate the capabilities of Gammapy or a given analysis method. Note that is is a binned simulation as is e.g. done also in Sherpa for Chandra, not an event sampling and anbinned analysis as is done e.g. in the Fermi ST or ctools.
Imports and versions¶
[1]:
%matplotlib inline
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
[2]:
import numpy as np
import astropy.units as u
from astropy.coordinates import SkyCoord, Angle
from gammapy.irf import load_cta_irfs
from gammapy.maps import WcsGeom, MapAxis, WcsNDMap, Map
from gammapy.spectrum.models import PowerLaw
from gammapy.image.models import SkyGaussian
from gammapy.cube.models import SkyModel, SkyModels
from gammapy.cube import MapFit, MapEvaluator, PSFKernel
from gammapy.cube import make_map_exposure_true_energy, make_map_background_irf
[3]:
!gammapy info --no-envvar --no-dependencies --no-system
Gammapy package:
path : /Users/jer/git/gammapy/gammapy/gammapy
version : 0.10
githash : c6bfb5371a5a1682cea9aaf56ebedb3c42010a43
Simulate¶
[4]:
filename = (
"$GAMMAPY_DATA/cta-1dc/caldb/data/cta/1dc/bcf/South_z20_50h/irf_file.fits"
)
irfs = load_cta_irfs(filename)
[5]:
# Define sky model to simulate the data
spatial_model = SkyGaussian(lon_0="0.2 deg", lat_0="0.1 deg", sigma="0.3 deg")
spectral_model = PowerLaw(
index=3, amplitude="1e-11 cm-2 s-1 TeV-1", reference="1 TeV"
)
sky_model = SkyModel(
spatial_model=spatial_model, spectral_model=spectral_model
)
print(sky_model)
SkyModel
Parameters:
name value error unit min max frozen
--------- --------- ----- -------------- --------- --- ------
lon_0 2.000e-01 nan deg nan nan False
lat_0 1.000e-01 nan deg nan nan False
sigma 3.000e-01 nan deg 0.000e+00 nan False
index 3.000e+00 nan nan nan False
amplitude 1.000e-11 nan cm-2 s-1 TeV-1 nan nan False
reference 1.000e+00 nan TeV nan nan True
[6]:
# Define map geometry
axis = MapAxis.from_edges(
np.logspace(-1.0, 1.0, 10), unit="TeV", name="energy", interp="log"
)
geom = WcsGeom.create(
skydir=(0, 0), binsz=0.02, width=(5, 4), coordsys="GAL", axes=[axis]
)
[7]:
# Define some observation parameters
# Here we just have a single observation,
# we are not simulating many pointings / observations
pointing = SkyCoord(1, 0.5, unit="deg", frame="galactic")
livetime = 1 * u.hour
offset_max = 2 * u.deg
offset = Angle("2 deg")
[8]:
exposure = make_map_exposure_true_energy(
pointing=pointing, livetime=livetime, aeff=irfs["aeff"], geom=geom
)
exposure.slice_by_idx({"energy": 3}).plot(add_cbar=True);
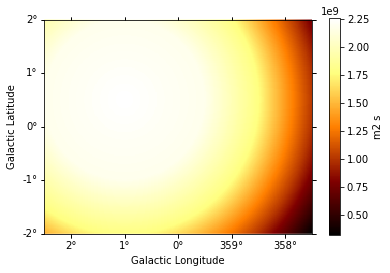
[9]:
background = make_map_background_irf(
pointing=pointing, ontime=livetime, bkg=irfs["bkg"], geom=geom
)
background.slice_by_idx({"energy": 3}).plot(add_cbar=True);
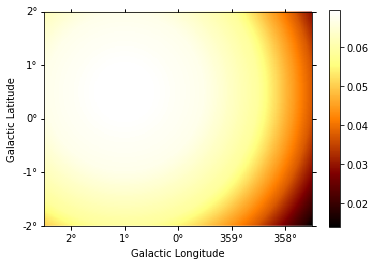
[10]:
psf = irfs["psf"].to_energy_dependent_table_psf(theta=offset)
psf_kernel = PSFKernel.from_table_psf(psf, geom, max_radius=0.3 * u.deg)
psf_kernel.psf_kernel_map.sum_over_axes().plot(stretch="log");
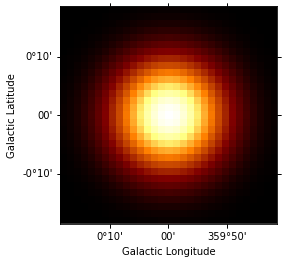
[11]:
energy = axis.edges * axis.unit
edisp = irfs["edisp"].to_energy_dispersion(
offset, e_reco=energy, e_true=energy
)
edisp.plot_matrix();
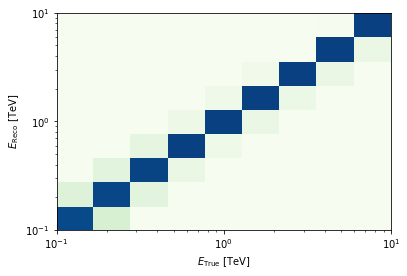
[12]:
%%time
# The idea is that we have this class that can compute `npred`
# maps, i.e. "predicted counts per pixel" given the model and
# the observation infos: exposure, background, PSF and EDISP
evaluator = MapEvaluator(
model=sky_model,
exposure=exposure,
background=background,
psf=psf_kernel,
edisp=edisp,
)
CPU times: user 14 µs, sys: 0 ns, total: 14 µs
Wall time: 18.1 µs
[13]:
# Accessing and saving a lot of the following maps is for debugging.
# Just for a simulation one doesn't need to store all these things.
# dnde = evaluator.compute_dnde()
# flux = evaluator.compute_flux()
npred = evaluator.compute_npred()
npred_map = WcsNDMap(geom, npred)
[14]:
npred_map.sum_over_axes().plot(add_cbar=True);
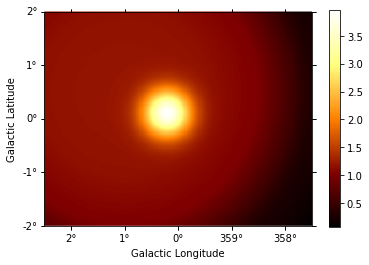
[15]:
# This one line is the core of how to simulate data when
# using binned simulation / analysis: you Poisson fluctuate
# npred to obtain simulated observed counts.
# Compute counts as a Poisson fluctuation
rng = np.random.RandomState(seed=42)
counts = rng.poisson(npred)
counts_map = WcsNDMap(geom, counts)
[16]:
counts_map.sum_over_axes().plot();
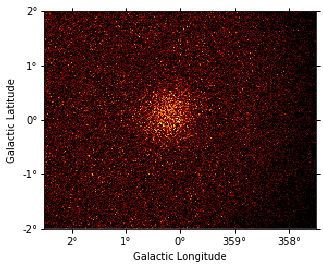
Fit¶
Now let’s analyse the simulated data. Here we just fit it again with the same model we had before, but you could do any analysis you like here, e.g. fit a different model, or do a region-based analysis, …
[17]:
# Define sky model to fit the data
spatial_model = SkyGaussian(lon_0="0 deg", lat_0="0 deg", sigma="1 deg")
spectral_model = PowerLaw(
index=2, amplitude="1e-11 cm-2 s-1 TeV-1", reference="1 TeV"
)
model = SkyModel(spatial_model=spatial_model, spectral_model=spectral_model)
# Impose that specrtal index remains within limits
spectral_model.parameters["index"].min = 0.0
spectral_model.parameters["index"].max = 10.0
print(model)
SkyModel
Parameters:
name value error unit min max frozen
--------- --------- ----- -------------- --------- --------- ------
lon_0 0.000e+00 nan deg nan nan False
lat_0 0.000e+00 nan deg nan nan False
sigma 1.000e+00 nan deg 0.000e+00 nan False
index 2.000e+00 nan 0.000e+00 1.000e+01 False
amplitude 1.000e-11 nan cm-2 s-1 TeV-1 nan nan False
reference 1.000e+00 nan TeV nan nan True
[18]:
%%time
fit = MapFit(
model=model,
counts=counts_map,
exposure=exposure,
background=background,
psf=psf_kernel,
)
result = fit.run(optimize_opts={"print_level": 1})
| FCN = 237085.25428198403 | TOTAL NCALL = 320 | NCALLS = 320 |
| EDM = 9.211816834617653e-06 | GOAL EDM = 1e-05 | UP = 1.0 |
| Valid | Valid Param | Accurate Covar | PosDef | Made PosDef |
| True | True | True | True | False |
| Hesse Fail | HasCov | Above EDM | Reach calllim | |
| False | True | False | False |
| + | Name | Value | Hesse Error | Minos Error- | Minos Error+ | Limit- | Limit+ | Fixed? |
| 0 | par_000_lon_0 | 0.198552 | 0.00848826 | No | ||||
| 1 | par_001_lat_0 | 0.0940465 | 0.00845781 | No | ||||
| 2 | par_002_sigma | 0.297597 | 0.00571018 | 0 | No | |||
| 3 | par_003_index | 3.00406 | 0.028128 | 0 | 10 | No | ||
| 4 | par_004_amplitude | 0.978708 | 0.0456659 | No | ||||
| 5 | par_005_reference | 1 | 1 | Yes |
CPU times: user 16.8 s, sys: 519 ms, total: 17.3 s
Wall time: 17.5 s
True model:
[19]:
print(sky_model)
SkyModel
Parameters:
name value error unit min max frozen
--------- --------- ----- -------------- --------- --- ------
lon_0 2.000e-01 nan deg nan nan False
lat_0 1.000e-01 nan deg nan nan False
sigma 3.000e-01 nan deg 0.000e+00 nan False
index 3.000e+00 nan nan nan False
amplitude 1.000e-11 nan cm-2 s-1 TeV-1 nan nan False
reference 1.000e+00 nan TeV nan nan True
Best-fit model:
[20]:
print(result.model)
SkyModel
Parameters:
name value error unit min max frozen
--------- --------- ----- -------------- --------- --------- ------
lon_0 1.986e-01 nan deg nan nan False
lat_0 9.405e-02 nan deg nan nan False
sigma 2.976e-01 nan deg 0.000e+00 nan False
index 3.004e+00 nan 0.000e+00 1.000e+01 False
amplitude 9.787e-12 nan cm-2 s-1 TeV-1 nan nan False
reference 1.000e+00 nan TeV nan nan True
[21]:
# TODO: show e.g. how to make a residual image