Note
Go to the end to download the full example code or to run this example in your browser via Binder
Dark matter spatial and spectral models#
Convenience methods for dark matter high level analyses.
Introduction#
Gammapy has some convenience methods for dark matter analyses in
darkmatter. These include J-Factor computation and
calculation the expected gamma flux for a number of annihilation
channels. They are presented in this notebook.
The basic concepts of indirect dark matter searches, however, are not explained. So this is aimed at people who already know what the want to do. A good introduction to indirect dark matter searches is given for example in https://arxiv.org/pdf/1012.4515.pdf (Chapter 1 and 5)
Setup#
As always, we start with some setup for the notebook, and with imports.
import numpy as np
import astropy.units as u
from astropy.coordinates import SkyCoord
from regions import CircleSkyRegion, RectangleSkyRegion
# %matplotlib inline
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.colors import LogNorm
from gammapy.astro.darkmatter import (
DarkMatterAnnihilationSpectralModel,
JFactory,
PrimaryFlux,
profiles,
)
from gammapy.maps import WcsGeom, WcsNDMap
Check setup#
from gammapy.utils.check import check_tutorials_setup
check_tutorials_setup()
System:
python_executable : /home/runner/work/gammapy-docs/gammapy-docs/gammapy/.tox/build_docs/bin/python
python_version : 3.9.16
machine : x86_64
system : Linux
Gammapy package:
version : 1.1
path : /home/runner/work/gammapy-docs/gammapy-docs/gammapy/.tox/build_docs/lib/python3.9/site-packages/gammapy
Other packages:
numpy : 1.24.3
scipy : 1.10.1
astropy : 5.2.2
regions : 0.7
click : 8.1.3
yaml : 6.0
IPython : 8.14.0
jupyterlab : not installed
matplotlib : 3.7.1
pandas : not installed
healpy : 1.16.2
iminuit : 2.21.3
sherpa : 4.15.1
naima : 0.10.0
emcee : 3.1.4
corner : 2.2.2
ray : 2.5.0
Gammapy environment variables:
GAMMAPY_DATA : /home/runner/work/gammapy-docs/gammapy-docs/gammapy-datasets/1.1
Profiles#
The following dark matter profiles are currently implemented. Each model
can be scaled to a given density at a certain distance. These parameters
are controlled by LOCAL_DENSITY and
DISTANCE_GC
profiles.DMProfile.__subclasses__()
for profile in profiles.DMProfile.__subclasses__():
p = profile()
p.scale_to_local_density()
radii = np.logspace(-3, 2, 100) * u.kpc
plt.plot(radii, p(radii), label=p.__class__.__name__)
plt.loglog()
plt.axvline(8.5, linestyle="dashed", color="black", label="local density")
plt.legend()
plt.show()
print("LOCAL_DENSITY:", profiles.DMProfile.LOCAL_DENSITY)
print("DISTANCE_GC:", profiles.DMProfile.DISTANCE_GC)
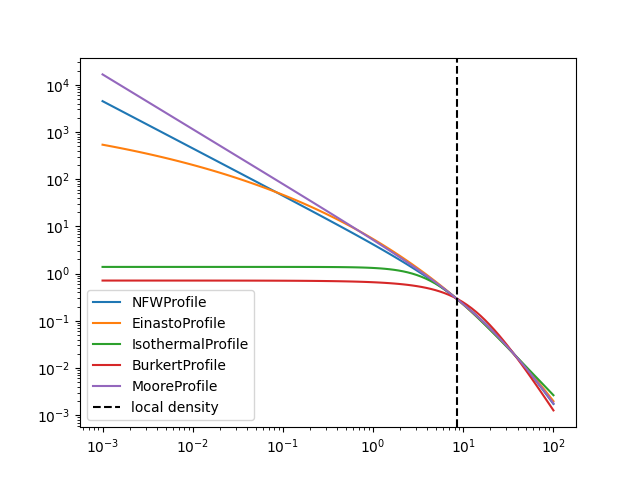
LOCAL_DENSITY: 0.3 GeV / cm3
DISTANCE_GC: 8.33 kpc
J Factors#
There are utilities to compute J-Factor maps that can serve as a basis to compute J-Factors for certain regions. In the following we compute a J-Factor map for the Galactic Centre region
profile = profiles.NFWProfile(r_s=20 * u.kpc)
# Adopt standard values used in HESS
profiles.DMProfile.DISTANCE_GC = 8.5 * u.kpc
profiles.DMProfile.LOCAL_DENSITY = 0.39 * u.Unit("GeV / cm3")
profile.scale_to_local_density()
position = SkyCoord(0.0, 0.0, frame="galactic", unit="deg")
geom = WcsGeom.create(binsz=0.05, skydir=position, width=3.0, frame="galactic")
jfactory = JFactory(geom=geom, profile=profile, distance=profiles.DMProfile.DISTANCE_GC)
jfact = jfactory.compute_jfactor()
jfact_map = WcsNDMap(geom=geom, data=jfact.value, unit=jfact.unit)
plt.figure()
ax = jfact_map.plot(cmap="viridis", norm=LogNorm(), add_cbar=True)
plt.title(f"J-Factor [{jfact_map.unit}]")
# 1 deg circle usually used in H.E.S.S. analyses without the +/- 0.3 deg band around the plane
sky_reg = CircleSkyRegion(center=position, radius=1 * u.deg)
pix_reg = sky_reg.to_pixel(wcs=geom.wcs)
pix_reg.plot(ax=ax, facecolor="none", edgecolor="red", label="1 deg circle")
sky_reg_rec = RectangleSkyRegion(center=position, height=0.6 * u.deg, width=2 * u.deg)
pix_reg_rec = sky_reg_rec.to_pixel(wcs=geom.wcs)
pix_reg_rec.plot(ax=ax, facecolor="none", edgecolor="orange", label="+/- 0.3 deg band")
plt.legend()
plt.show()
# NOTE: https://arxiv.org/abs/1607.08142 quote 2.67e21
total_jfact = (
pix_reg.to_mask().multiply(jfact).sum()
- pix_reg_rec.to_mask().multiply(jfact).sum()
)
total_jfact = (
pix_reg.to_mask().multiply(jfact).sum()
- pix_reg_rec.to_mask().multiply(jfact).sum()
)
print(
"J-factor in 1 deg circle without the +/- 0.3 deg band around GC assuming a "
f"{profile.__class__.__name__} is {total_jfact:.3g}"
)
![J-Factor [GeV2 / cm5]](../../_images/sphx_glr_astro_dark_matter_002.png)
J-factor in 1 deg circle without the +/- 0.3 deg band around GC assuming a NFWProfile is 2.36e+21 GeV2 / cm5
Gamma-ray spectra at production#
The gamma-ray spectrum per annihilation is a further ingredient for a dark matter analysis. The following annihilation channels are supported. For more info see https://arxiv.org/pdf/1012.4515.pdf
fluxes = PrimaryFlux(mDM="1 TeV", channel="eL")
print(fluxes.allowed_channels)
fig, axes = plt.subplots(4, 1, figsize=(4, 16))
mDMs = [0.01, 0.1, 1, 10] * u.TeV
for mDM, ax in zip(mDMs, axes):
fluxes.mDM = mDM
ax.set_title(rf"m$_{{\mathrm{{DM}}}}$ = {mDM}")
ax.set_yscale("log")
ax.set_ylabel("dN/dE")
for channel in ["tau", "mu", "b", "Z"]:
fluxes.channel = channel
fluxes.table_model.plot(
energy_bounds=[mDM / 100, mDM],
ax=ax,
label=channel,
yunits=u.Unit("1/GeV"),
)
axes[0].legend()
plt.subplots_adjust(hspace=0.9)
plt.show()
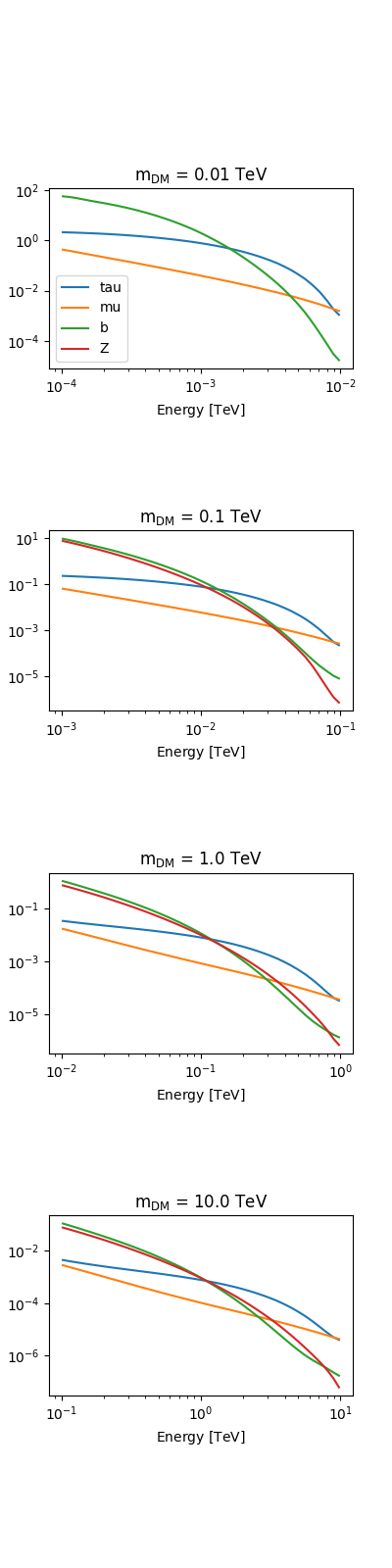
['eL', 'eR', 'e', 'muL', 'muR', 'mu', 'tauL', 'tauR', 'tau', 'q', 'c', 'b', 't', 'WL', 'WT', 'W', 'ZL', 'ZT', 'Z', 'g', 'gamma', 'h', 'nu_e', 'nu_mu', 'nu_tau', 'V->e', 'V->mu', 'V->tau']
Flux maps#
Finally flux maps can be produced like this:
channel = "Z"
massDM = 10 * u.TeV
diff_flux = DarkMatterAnnihilationSpectralModel(mass=massDM, channel=channel)
int_flux = (
jfact * diff_flux.integral(energy_min=0.1 * u.TeV, energy_max=10 * u.TeV)
).to("cm-2 s-1")
flux_map = WcsNDMap(geom=geom, data=int_flux.value, unit="cm-2 s-1")
plt.figure()
ax = flux_map.plot(cmap="viridis", norm=LogNorm(), add_cbar=True)
plt.title(
f"Flux [{int_flux.unit}]\n m$_{{DM}}$={fluxes.mDM.to('TeV')}, channel={fluxes.channel}"
)
plt.show()
![Flux [1 / (cm2 s)] m$_{DM}$=10.0 TeV, channel=Z](../../_images/sphx_glr_astro_dark_matter_004.png)
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 15.024 seconds)