This is a fixed-text formatted version of a Jupyter notebook
You may download all the notebooks as a tar file.
Source files: sed_fitting.ipynb | sed_fitting.py
Flux point fitting#
Prerequisites#
Some knowledge about retrieving information from catalogs, see the catalogs tutorial
Context#
Some high level studies do not rely on reduced datasets with their IRFs but directly on higher level products such as flux points. This is not ideal because flux points already contain some hypothesis for the underlying spectral shape and the uncertainties they carry are usually simplified (e.g. symmetric gaussian errors). Yet, this is an efficient way to combine heterogeneous data.
Objective: fit spectral models to combined Fermi-LAT and IACT flux points.
Proposed approach#
Here we will load, the spectral points from Fermi-LAT and TeV catalogs and fit them with various spectral models to find the best representation of the wide band spectrum.
The central class we’re going to use for this example analysis is:
In addition we will work with the following data classes:
And the following spectral model classes:
Setup#
Let us start with the usual IPython notebook and Python imports:
[1]:
%matplotlib inline
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
[2]:
from astropy import units as u
from gammapy.modeling.models import (
PowerLawSpectralModel,
ExpCutoffPowerLawSpectralModel,
LogParabolaSpectralModel,
SkyModel,
)
from gammapy.estimators import FluxPoints
from gammapy.datasets import FluxPointsDataset, Datasets
from gammapy.catalog import CATALOG_REGISTRY
from gammapy.modeling import Fit
Load spectral points#
For this analysis we choose to work with the source ‘HESS J1507-622’ and the associated Fermi-LAT sources ‘3FGL J1506.6-6219’ and ‘3FHL J1507.9-6228e’. We load the source catalogs, and then access source of interest by name:
[3]:
catalog_3fgl = CATALOG_REGISTRY.get_cls("3fgl")()
catalog_3fhl = CATALOG_REGISTRY.get_cls("3fhl")()
catalog_gammacat = CATALOG_REGISTRY.get_cls("gamma-cat")()
[4]:
source_fermi_3fgl = catalog_3fgl["3FGL J1506.6-6219"]
source_fermi_3fhl = catalog_3fhl["3FHL J1507.9-6228e"]
source_gammacat = catalog_gammacat["HESS J1507-622"]
The corresponding flux points data can be accessed with .flux_points attribute:
[5]:
dataset_gammacat = FluxPointsDataset(
data=source_gammacat.flux_points, name="gammacat"
)
dataset_gammacat.data.to_table(sed_type="dnde", formatted=True)
[5]:
| e_ref | dnde | dnde_errp | dnde_errn | is_ul |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TeV | 1 / (cm2 s TeV) | 1 / (cm2 s TeV) | 1 / (cm2 s TeV) | |
| float64 | float64 | float64 | float64 | bool |
| 0.861 | 2.291e-12 | 8.955e-13 | 8.705e-13 | False |
| 1.562 | 6.982e-13 | 2.304e-13 | 2.204e-13 | False |
| 2.764 | 1.691e-13 | 7.188e-14 | 6.759e-14 | False |
| 4.892 | 7.729e-14 | 2.607e-14 | 2.401e-14 | False |
| 9.989 | 1.033e-14 | 5.642e-15 | 5.063e-15 | False |
| 27.040 | 7.450e-16 | 7.260e-16 | 5.721e-16 | False |
[6]:
dataset_3fgl = FluxPointsDataset(
data=source_fermi_3fgl.flux_points, name="3fgl"
)
dataset_3fgl.data.to_table(sed_type="dnde", formatted=True)
[6]:
| e_ref | e_min | e_max | dnde | dnde_errp | dnde_errn | dnde_ul | sqrt_ts | is_ul |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MeV | MeV | MeV | 1 / (cm2 MeV s) | 1 / (cm2 MeV s) | 1 / (cm2 MeV s) | 1 / (cm2 MeV s) | ||
| float64 | float64 | float64 | float64 | float64 | float64 | float64 | float32 | bool |
| 173.205 | 100.000 | 300.000 | 1.798e-10 | 5.566e-11 | 5.710e-11 | nan | 2.843 | False |
| 547.723 | 300.000 | 1000.000 | 2.171e-13 | 1.689e-12 | nan | 3.595e-12 | 0.000 | True |
| 1732.051 | 1000.000 | 3000.000 | 2.528e-13 | 1.058e-13 | 9.991e-14 | nan | 2.661 | False |
| 5477.226 | 3000.000 | 10000.000 | 2.654e-14 | 8.936e-15 | 7.932e-15 | nan | 4.265 | False |
| 31622.777 | 10000.000 | 100000.000 | 1.274e-15 | 4.237e-16 | 3.658e-16 | nan | 5.774 | False |
[7]:
dataset_3fhl = FluxPointsDataset(
data=source_fermi_3fhl.flux_points, name="3fhl"
)
dataset_3fhl.data.to_table(sed_type="dnde", formatted=True)
[7]:
| e_ref | e_min | e_max | dnde | dnde_errp | dnde_errn | dnde_ul | sqrt_ts | is_ul |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GeV | GeV | GeV | 1 / (cm2 GeV s) | 1 / (cm2 GeV s) | 1 / (cm2 GeV s) | 1 / (cm2 GeV s) | ||
| float64 | float64 | float64 | float64 | float64 | float64 | float64 | float32 | bool |
| 14.142 | 10.000 | 20.000 | 9.288e-12 | 2.343e-12 | 2.128e-12 | nan | 5.660 | False |
| 31.623 | 20.000 | 50.000 | 2.777e-12 | 6.572e-13 | 5.818e-13 | nan | 6.940 | False |
| 86.603 | 50.000 | 150.000 | 2.335e-13 | 1.055e-13 | 8.554e-14 | nan | 3.835 | False |
| 273.861 | 150.000 | 500.000 | 6.411e-14 | 2.697e-14 | 2.133e-14 | nan | 5.697 | False |
| 1000.000 | 500.000 | 2000.000 | 9.188e-21 | 4.034e-15 | nan | 8.068e-15 | 0.000 | True |
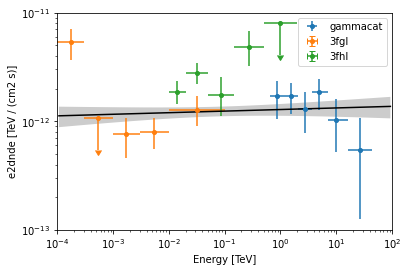
Power Law Fit#
First we start with fitting a simple gammapy.modeling.models.PowerLawSpectralModel.
[8]:
pwl = PowerLawSpectralModel(
index=2, amplitude="1e-12 cm-2 s-1 TeV-1", reference="1 TeV"
)
model = SkyModel(spectral_model=pwl, name="j1507-pl")
After creating the model we run the fit by passing the 'flux_points' and 'model' objects:
[9]:
datasets = Datasets([dataset_gammacat, dataset_3fgl, dataset_3fhl])
datasets.models = model
print(datasets)
Datasets
--------
Dataset 0:
Type : FluxPointsDataset
Name : gammacat
Instrument :
Models : ['j1507-pl']
Dataset 1:
Type : FluxPointsDataset
Name : 3fgl
Instrument :
Models : ['j1507-pl']
Dataset 2:
Type : FluxPointsDataset
Name : 3fhl
Instrument :
Models : ['j1507-pl']
[10]:
fitter = Fit()
result_pwl = fitter.run(datasets=datasets)
And print the result:
[11]:
print(result_pwl)
OptimizeResult
backend : minuit
method : migrad
success : True
message : Optimization terminated successfully.
nfev : 40
total stat : 28.29
CovarianceResult
backend : minuit
method : hesse
success : True
message : Hesse terminated successfully.
[12]:
print(model)
SkyModel
Name : j1507-pl
Datasets names : None
Spectral model type : PowerLawSpectralModel
Spatial model type :
Temporal model type :
Parameters:
index : 1.985 +/- 0.03
amplitude : 1.28e-12 +/- 1.6e-13 1 / (cm2 s TeV)
reference (frozen): 1.000 TeV
Finally we plot the data points and the best fit model:
[13]:
ax = plt.subplot()
ax.yaxis.set_units(u.Unit("TeV cm-2 s-1"))
kwargs = {"ax": ax, "sed_type": "e2dnde"}
for d in datasets:
d.data.plot(label=d.name, **kwargs)
energy_bounds = [1e-4, 1e2] * u.TeV
pwl.plot(energy_bounds=energy_bounds, color="k", **kwargs)
pwl.plot_error(energy_bounds=energy_bounds, **kwargs)
ax.set_ylim(1e-13, 1e-11)
ax.set_xlim(energy_bounds)
ax.legend()
[13]:
<matplotlib.legend.Legend at 0x13f3cbb20>
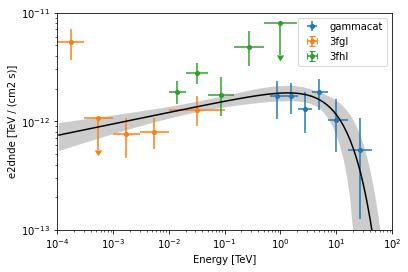
Exponential Cut-Off Powerlaw Fit#
Next we fit an gammapy.modeling.models.ExpCutoffPowerLawSpectralModel law to the data.
[14]:
ecpl = ExpCutoffPowerLawSpectralModel(
index=1.8,
amplitude="2e-12 cm-2 s-1 TeV-1",
reference="1 TeV",
lambda_="0.1 TeV-1",
)
model = SkyModel(spectral_model=ecpl, name="j1507-ecpl")
We run the fitter again by passing the flux points and the model instance:
[15]:
datasets.models = model
result_ecpl = fitter.run(datasets=datasets)
print(model)
SkyModel
Name : j1507-ecpl
Datasets names : None
Spectral model type : ExpCutoffPowerLawSpectralModel
Spatial model type :
Temporal model type :
Parameters:
index : 1.894 +/- 0.05
amplitude : 1.96e-12 +/- 3.9e-13 1 / (cm2 s TeV)
reference (frozen): 1.000 TeV
lambda_ : 0.078 +/- 0.05 1 / TeV
alpha (frozen): 1.000
We plot the data and best fit model:
[16]:
ax = plt.subplot()
kwargs = {"ax": ax, "sed_type": "e2dnde"}
ax.yaxis.set_units(u.Unit("TeV cm-2 s-1"))
for d in datasets:
d.data.plot(label=d.name, **kwargs)
ecpl.plot(energy_bounds=energy_bounds, color="k", **kwargs)
ecpl.plot_error(energy_bounds=energy_bounds, **kwargs)
ax.set_ylim(1e-13, 1e-11)
ax.set_xlim(energy_bounds)
ax.legend()
[16]:
<matplotlib.legend.Legend at 0x13f8b3b80>
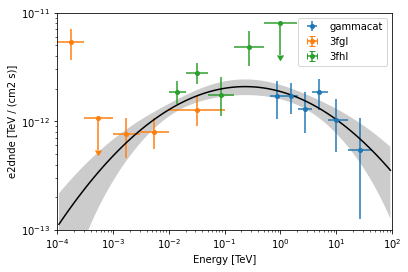
Log-Parabola Fit#
Finally we try to fit a gammapy.modeling.models.LogParabolaSpectralModel model:
[17]:
log_parabola = LogParabolaSpectralModel(
alpha=2, amplitude="1e-12 cm-2 s-1 TeV-1", reference="1 TeV", beta=0.1
)
model = SkyModel(spectral_model=log_parabola, name="j1507-lp")
[18]:
datasets.models = model
result_log_parabola = fitter.run(datasets=datasets)
print(model)
SkyModel
Name : j1507-lp
Datasets names : None
Spectral model type : LogParabolaSpectralModel
Spatial model type :
Temporal model type :
Parameters:
amplitude : 1.88e-12 +/- 2.8e-13 1 / (cm2 s TeV)
reference (frozen): 1.000 TeV
alpha : 2.144 +/- 0.07
beta : 0.049 +/- 0.02
[19]:
ax = plt.subplot()
kwargs = {"ax": ax, "sed_type": "e2dnde"}
ax.yaxis.set_units(u.Unit("TeV cm-2 s-1"))
for d in datasets:
d.data.plot(label=d.name, **kwargs)
log_parabola.plot(energy_bounds=energy_bounds, color="k", **kwargs)
log_parabola.plot_error(energy_bounds=energy_bounds, **kwargs)
ax.set_ylim(1e-13, 1e-11)
ax.set_xlim(energy_bounds)
ax.legend()
[19]:
<matplotlib.legend.Legend at 0x13ead8c40>
Exercises#
Fit a
gammapy.modeling.models.PowerLaw2SpectralModelandgammapy.modeling.models.ExpCutoffPowerLaw3FGLSpectralModelto the same data.Fit a
gammapy.modeling.models.ExpCutoffPowerLawSpectralModelmodel to Vela X (‘HESS J0835-455’) only and check if the best fit values correspond to the values given in the Gammacat catalog
What next?#
This was an introduction to SED fitting in Gammapy.
If you would like to learn how to perform a full Poisson maximum likelihood spectral fit, please check out the spectrum analysis tutorial.
To learn how to combine heterogeneous datasets to perform a multi-instrument forward-folding fit see the MWL analysis tutorial
[ ]:
