Data access and selection (DL3)#
IACT data is typically structured in “observations”, which define a given time interval during with the instrument response is considered stable.
gammapy.data currently contains the EventList class,
as well as classes for IACT data and observation handling.
The main classes in Gammapy to access the DL3 data library are the
DataStore and Observation.
They are used to store and retrieve dynamically the datasets
relevant to any observation (event list in the form of an EventList,
IRFs see Instrument Response Functions (DL3) and other relevant information).
Once some observation selection has been selected, the user can build a list of observations:
a Observations object, which will be used for the data reduction process.
Getting started with data#
You can use the EventList class to load IACT gamma-ray event lists:
from gammapy.data import EventList
filename = '$GAMMAPY_DATA/hess-dl3-dr1/data/hess_dl3_dr1_obs_id_023523.fits.gz'
events = EventList.read(filename)
To load Fermi-LAT event lists, use the EventListLAT class:
from gammapy.data import EventList
filename = "$GAMMAPY_DATA/fermi-3fhl-gc/fermi-3fhl-gc-events.fits.gz"
events = EventList.read(filename)
The other main class in gammapy.data is the DataStore, which makes it easy
to load IACT data. E.g. an alternative way to load the events for observation ID 23523 is this:
from gammapy.data import DataStore
data_store = DataStore.from_dir('$GAMMAPY_DATA/hess-dl3-dr1')
events = data_store.obs(23523).events
The index tables#
A typical way to organize the files relevant to the data we are interested in are the index tables. There are two tables:
Observation index table: this table collects the information on each observation or run, with meta data about each of them, such as the pointing direction, the duration, the run ID…
HDU index table: this table provides, for each observation listed in the index table, the location of the corresponding data and instrument response files.
A DataStore can then be created by providing each of these two tables in the same file with from_file(), or instead by the directory where they can be found with from_dir() as shown above.
More details on these tables and their content can be found in https://gamma-astro-data-formats.readthedocs.io/en/latest/data_storage/index.html.
Working with event lists#
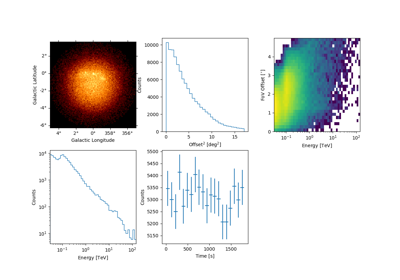
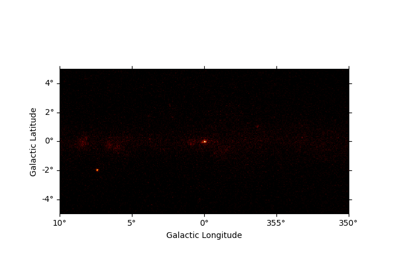
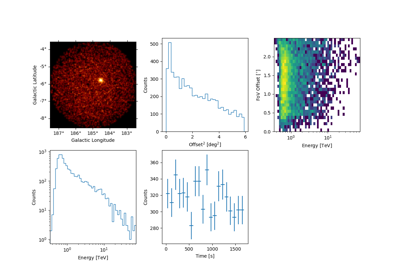
To take a quick look at the events inside the list, one can use peek()
from gammapy.data import EventList
filename = '$GAMMAPY_DATA/hess-dl3-dr1/data/hess_dl3_dr1_obs_id_023523.fits.gz'
events = EventList.read(filename)
events.peek()
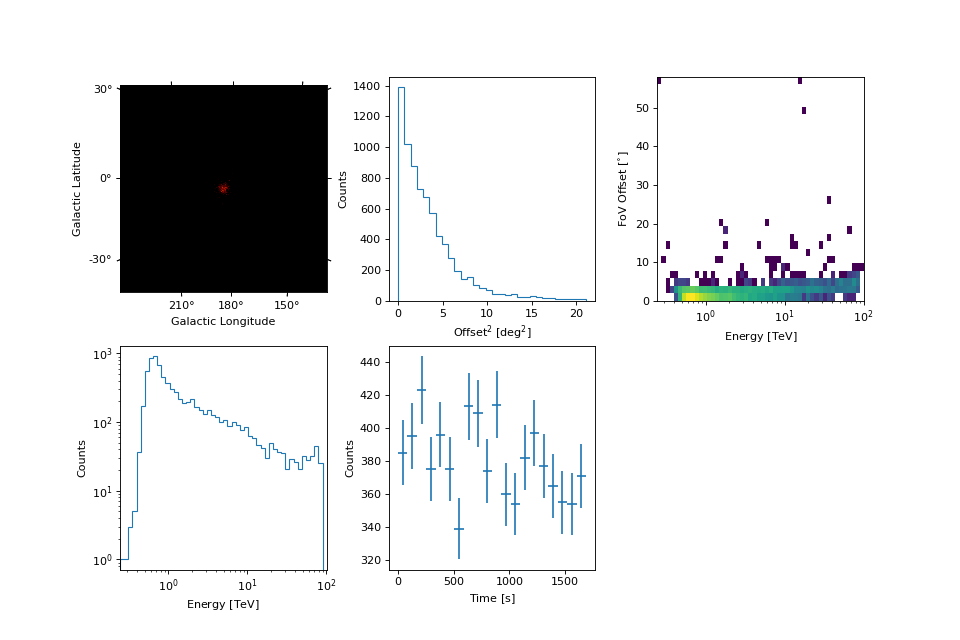
Events can be selected based on any of their properties, with dedicated functions existing for energy, time, offset from pointing position and the selection of events in a particular region of the sky.
import astropy.units as u
from astropy.time import Time
from gammapy.data import EventList
filename = '$GAMMAPY_DATA/hess-dl3-dr1/data/hess_dl3_dr1_obs_id_023523.fits.gz'
events = EventList.read(filename)
# Select events based on energy
selected_energy = events.select_energy([1*u.TeV, 1.2*u.TeV])
# Select events based on time
t_start = Time(57185, format='mjd')
t_stop = Time(57185.5, format='mjd')
selected_time = events.select_time([t_start, t_stop])
# Select events based on offset
selected_offset = events.select_offset([1*u.deg, 2*u.deg])
# Select events from a region in the sky
selected_region = events.select_region("icrs;circle(86.3,22.01,3)")
# Finally one can select events based on any other of the columns of the `EventList.table`
selected_id = events.select_parameter('EVENT_ID', (5407363826067,5407363826070))
Combining event lists and GTIs#
Both event lists and GTIs can be stacked into a larger one. An EventList can also be created from_stack, that is,
from a list of EventList objects.
from gammapy.data import EventList, GTI
filename_1 = '$GAMMAPY_DATA/hess-dl3-dr1/data/hess_dl3_dr1_obs_id_023523.fits.gz'
filename_2 = '$GAMMAPY_DATA/hess-dl3-dr1/data/hess_dl3_dr1_obs_id_023526.fits.gz'
events_1 = EventList.read(filename_1)
events_2 = EventList.read(filename_2)
gti_1 = GTI.read(filename_1)
gti_2 = GTI.read(filename_2)
# stack in place, now the _1 object contains the information of both
gti_1.stack(gti_2)
events_1.stack(events_2)
# or instead create a new event list from the other two
combined_events = EventList.from_stack([events_1, events_2])
Writing event lists and GTIs to file#
To write the events or GTIs separately, one can just save the underlying
astropy.table.Table. To have an event file written in a correct DL3 format, it is
necessary to utilise the write method available for`~gammapy.data.Observation`.
It will write the EventList and their associated GTIs together in the
same FITS file according to the format specifications. To avoid writing IRFs along the
EventList one has to set include_irfs to False. See the example below:
from gammapy.data import EventList, GTI, Observation
filename = "$GAMMAPY_DATA/hess-dl3-dr1/data/hess_dl3_dr1_obs_id_023523.fits.gz"
events = EventList.read(filename)
gti = GTI.read(filename)
# Save separately
gti.write("test_gti.fits.gz")
# Save together. First initiate an Observation object
obs = Observation(gti=gti, events=events)
obs.write("test_events_with_GTI.fits.gz", include_irfs=False)
Using gammapy.data#
Examples using gammapy.data.EventList#
Sample a source with energy-dependent temporal evolution
Examples using gammapy.data.DataStore#
Spectral analysis with energy-dependent directional cuts