This is a fixed-text formatted version of a Jupyter notebook
You may download all the notebooks as a tar file.
Source files: light_curve_simulation.ipynb | light_curve_simulation.py
Simulating and fitting a time varying source#
Prerequisites#
To understand how a single binned simulation works, please refer to spectrum_simulation simulate_3d for 1D and 3D simulations respectively.
For details of light curve extraction using gammapy, refer to the two tutorials light_curve and light_curve_flare
Context#
Frequently, studies of variable sources (eg: decaying GRB light curves, AGN flares, etc) require time variable simulations. For most use cases, generating an event list is an overkill, and it suffices to use binned simulations using a temporal model.
Objective: Simulate and fit a time decaying light curve of a source with CTA using the CTA 1DC response
Proposed approach#
We will simulate 10 spectral datasets within given time intervals (Good Time Intervals) following a given spectral (a power law) and temporal profile (an exponential decay, with a decay time of 6 hr ). These are then analysed using the light curve estimator to obtain flux points.
Modelling and fitting of lightcurves can be done either - directly on the output of the LighCurveEstimator (at the DL5 level) - fit the simulated datasets (at the DL4 level)
In summary, necessary steps are:
Choose observation parameters including a list of
gammapy.data.GTIDefine temporal and spectral models from :ref:model-gallery as per science case
Perform the simulation (in 1D or 3D)
Extract the light curve from the reduced dataset as shown in light curve notebook
Optionally, we show here how to fit the simulated datasets using a source model
Setup#
As usual, we’ll start with some general imports…
Setup#
[1]:
%matplotlib inline
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import astropy.units as u
from astropy.coordinates import SkyCoord
from astropy.time import Time
import logging
log = logging.getLogger(__name__)
And some gammapy specific imports
[2]:
from gammapy.data import Observation
from gammapy.irf import load_cta_irfs
from gammapy.datasets import SpectrumDataset, Datasets, FluxPointsDataset
from gammapy.modeling.models import (
PowerLawSpectralModel,
ExpDecayTemporalModel,
SkyModel,
)
from gammapy.maps import MapAxis, RegionGeom, TimeMapAxis
from gammapy.estimators import LightCurveEstimator
from gammapy.makers import SpectrumDatasetMaker
from gammapy.modeling import Fit
from gammapy.data import observatory_locations
We first define our preferred time format:
[3]:
TimeMapAxis.time_format = "iso"
Simulating a light curve#
We will simulate 10 spectra between 300 GeV and 10 TeV using an PowerLawSpectralModel and a ExpDecayTemporalModel. The important thing to note here is how to attach a different GTI to each dataset. Since we use spectrum datasets here, we will use a RegionGeom.
[4]:
# Loading IRFs
irfs = load_cta_irfs(
"$GAMMAPY_DATA/cta-1dc/caldb/data/cta/1dc/bcf/South_z20_50h/irf_file.fits"
)
Invalid unit found in background table! Assuming (s-1 MeV-1 sr-1)
[5]:
# Reconstructed and true energy axis
energy_axis = MapAxis.from_edges(
np.logspace(-0.5, 1.0, 10), unit="TeV", name="energy", interp="log"
)
energy_axis_true = MapAxis.from_edges(
np.logspace(-1.2, 2.0, 31), unit="TeV", name="energy_true", interp="log"
)
geom = RegionGeom.create("galactic;circle(0, 0, 0.11)", axes=[energy_axis])
[6]:
# Pointing position
pointing = SkyCoord(0.5, 0.5, unit="deg", frame="galactic")
Note that observations are usually conducted in Wobble mode, in which the source is not in the center of the camera. This allows to have a symmetrical sky position from which background can be estimated.
[7]:
# Define the source model: A combination of spectral and temporal model
gti_t0 = Time("2020-03-01")
spectral_model = PowerLawSpectralModel(
index=3, amplitude="1e-11 cm-2 s-1 TeV-1", reference="1 TeV"
)
temporal_model = ExpDecayTemporalModel(t0="6 h", t_ref=gti_t0.mjd * u.d)
model_simu = SkyModel(
spectral_model=spectral_model,
temporal_model=temporal_model,
name="model-simu",
)
/Users/terrier/Code/anaconda3/envs/gammapy-dev/lib/python3.8/site-packages/astropy/units/quantity.py:613: RuntimeWarning: overflow encountered in exp
result = super().__array_ufunc__(function, method, *arrays, **kwargs)
/Users/terrier/Code/anaconda3/envs/gammapy-dev/lib/python3.8/site-packages/astropy/units/quantity.py:613: RuntimeWarning: invalid value encountered in subtract
result = super().__array_ufunc__(function, method, *arrays, **kwargs)
[8]:
# Look at the model
model_simu.parameters.to_table()
[8]:
| type | name | value | unit | error | min | max | frozen | is_norm | link |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| str8 | str9 | float64 | str14 | int64 | float64 | float64 | bool | bool | str1 |
| spectral | index | 3.0000e+00 | 0.000e+00 | nan | nan | False | False | ||
| spectral | amplitude | 1.0000e-11 | cm-2 s-1 TeV-1 | 0.000e+00 | nan | nan | False | True | |
| spectral | reference | 1.0000e+00 | TeV | 0.000e+00 | nan | nan | True | False | |
| temporal | t0 | 6.0000e+00 | h | 0.000e+00 | nan | nan | False | False | |
| temporal | t_ref | 5.8909e+04 | d | 0.000e+00 | nan | nan | True | False |
Now, define the start and observation livetime wrt to the reference time, gti_t0
[9]:
n_obs = 10
tstart = gti_t0 + [1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 10, 20, 22, 23, 24] * u.h
lvtm = [55, 25, 26, 40, 40, 50, 40, 52, 43, 47] * u.min
Now perform the simulations
[10]:
datasets = Datasets()
empty = SpectrumDataset.create(
geom=geom, energy_axis_true=energy_axis_true, name="empty"
)
maker = SpectrumDatasetMaker(selection=["exposure", "background", "edisp"])
for idx in range(n_obs):
obs = Observation.create(
pointing=pointing,
livetime=lvtm[idx],
tstart=tstart[idx],
irfs=irfs,
reference_time=gti_t0,
obs_id=idx,
location=observatory_locations["cta_south"],
)
empty_i = empty.copy(name=f"dataset-{idx}")
dataset = maker.run(empty_i, obs)
dataset.models = model_simu
dataset.fake()
datasets.append(dataset)
The reduced datasets have been successfully simulated. Let’s take a quick look into our datasets.
[11]:
datasets.info_table()
[11]:
| name | counts | excess | sqrt_ts | background | npred | npred_background | npred_signal | exposure_min | exposure_max | livetime | ontime | counts_rate | background_rate | excess_rate | n_bins | n_fit_bins | stat_type | stat_sum |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| m2 s | m2 s | s | s | 1 / s | 1 / s | 1 / s | ||||||||||||
| str9 | int64 | float64 | float64 | float64 | float64 | float64 | float64 | float64 | float64 | float64 | float64 | float64 | float64 | float64 | int64 | int64 | str4 | float64 |
| dataset-0 | 829 | 808.6812133789062 | 67.31731458104936 | 20.318769454956055 | 20.318769469857216 | 20.318769454956055 | nan | 216137904.0 | 16025275392.0 | 3299.9999999999973 | 3300.0 | 0.25121212121212144 | 0.006157202865138204 | 0.24505491314512332 | 9 | 9 | cash | nan |
| dataset-1 | 330 | 320.7641959176923 | 41.4564216021322 | 9.235804082307682 | 332.1496126848936 | 9.235804082307682 | 322.91380860258596 | 98244500.93556362 | 7284216297.312286 | 1500.0000000000036 | 1500.0000000000036 | 0.21999999999999947 | 0.00615720272153844 | 0.213842797278461 | 9 | 9 | cash | -2053.5263391934623 |
| dataset-2 | 320 | 310.3947637544 | 40.28720068338956 | 9.60523624559999 | 293.48960245451894 | 9.60523624559999 | 283.884366208919 | 102174280.97298616 | 7575584949.204778 | 1560.0000000000036 | 1560.0000000000036 | 0.20512820512820465 | 0.006157202721538441 | 0.1989710024066662 | 9 | 9 | cash | -1995.2213487608487 |
| dataset-3 | 320 | 305.22271346830775 | 36.847002227816574 | 14.777286531692258 | 321.7838592189118 | 14.777286531692258 | 307.00657268721955 | 157191201.49690142 | 11654746075.69963 | 2400.0 | 2400.0 | 0.13333333333333333 | 0.006157202721538441 | 0.1271761306117949 | 9 | 9 | cash | -1950.1409750273895 |
| dataset-4 | 213 | 198.22271346830775 | 27.20676640833841 | 14.777286531692258 | 200.9861855997861 | 14.777286531692258 | 186.2088990680938 | 157191201.49690142 | 11654746075.69963 | 2400.0 | 2400.0 | 0.08875 | 0.006157202721538441 | 0.08259279727846155 | 9 | 9 | cash | -1137.4784918388684 |
| dataset-5 | 190 | 171.52839183538467 | 23.294701482664998 | 18.471608164615322 | 182.99944247949256 | 18.471608164615322 | 164.5278343148772 | 196489001.87112677 | 14568432594.624538 | 3000.0 | 3000.0 | 0.06333333333333334 | 0.006157202721538441 | 0.05717613061179489 | 9 | 9 | cash | -1016.7012114582753 |
| dataset-6 | 38 | 23.22271346830774 | 5.033505913945236 | 14.777286531692258 | 39.977920628250665 | 14.777286531692258 | 25.20063409655841 | 157191201.49690142 | 11654746075.69963 | 2400.0 | 2400.0 | 0.015833333333333335 | 0.006157202721538441 | 0.009676130611794892 | 9 | 9 | cash | -64.33017421792906 |
| dataset-7 | 51 | 31.789527508800063 | 6.00089086025525 | 19.210472491199937 | 42.30482855222412 | 19.210472491199937 | 23.094356061024193 | 204348561.94597185 | 15151169898.40952 | 3120.0 | 3120.0 | 0.016346153846153847 | 0.0061572027215384415 | 0.010188951124615405 | 9 | 9 | cash | -137.61176114657297 |
| dataset-8 | 31 | 15.114416978430823 | 3.350049342927064 | 15.885583021569177 | 32.249900287793274 | 15.885583021569177 | 16.36431726622409 | 168980541.609169 | 12528852031.377102 | 2580.0 | 2580.0 | 0.012015503875968992 | 0.006157202721538441 | 0.0058583011544305515 | 9 | 9 | cash | -53.98618916042473 |
| dataset-9 | 39 | 21.6366883252616 | 4.45470472668954 | 17.3633116747384 | 32.421834962248106 | 17.3633116747384 | 15.05852328750971 | 184699661.75885916 | 13694326638.947065 | 2820.0 | 2820.0 | 0.013829787234042552 | 0.006157202721538441 | 0.007672584512504113 | 9 | 9 | cash | -84.26051818568244 |
Extract the lightcurve#
This section uses standard light curve estimation tools for a 1D extraction. Only a spectral model needs to be defined in this case. Since the estimator returns the integrated flux separately for each time bin, the temporal model need not be accounted for at this stage. We extract the lightcurve in 3 energy binsç
[12]:
# Define the model:
spectral_model = PowerLawSpectralModel(
index=3, amplitude="1e-11 cm-2 s-1 TeV-1", reference="1 TeV"
)
model_fit = SkyModel(spectral_model=spectral_model, name="model-fit")
[13]:
# Attach model to all datasets
datasets.models = model_fit
[14]:
%%time
lc_maker_1d = LightCurveEstimator(
energy_edges=[0.3, 0.6, 1.0, 10] * u.TeV,
source="model-fit",
selection_optional=["ul"],
)
lc_1d = lc_maker_1d.run(datasets)
CPU times: user 26.1 s, sys: 238 ms, total: 26.3 s
Wall time: 30.1 s
[15]:
ax = lc_1d.plot(marker="o", axis_name="time", sed_type="flux")
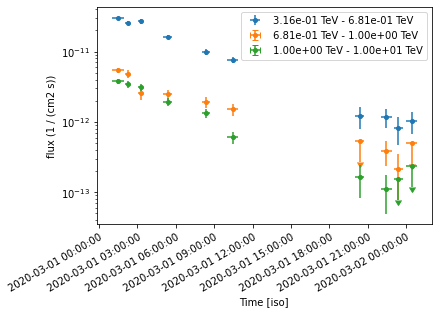
Fitting temporal models#
We have the reconstructed lightcurve at this point. Now we want to fit a profile to the obtained light curves, using a joint fitting across the different datasets, while simultaneously minimising across the temporal model parameters as well. The temporal models can be applied
directly on the obtained lightcurve
on the simulated datasets
Fitting the obtained light curve#
The fitting will proceed through a joint fit of the flux points. First, we need to obtain a set of FluxPointDatasets, one for each time bin
[16]:
## Create the datasets by iterating over the returned lightcurve
datasets = Datasets()
for idx, fp in enumerate(lc_1d.iter_by_axis(axis_name="time")):
dataset = FluxPointsDataset(data=fp, name=f"time-bin-{idx}")
datasets.append(dataset)
We will fit the amplitude, spectral index and the decay time scale. Note that t_ref should be fixed by default for the ExpDecayTemporalModel.
[17]:
# Define the model:
spectral_model1 = PowerLawSpectralModel(
index=2.0, amplitude="1e-12 cm-2 s-1 TeV-1", reference="1 TeV"
)
temporal_model1 = ExpDecayTemporalModel(t0="10 h", t_ref=gti_t0.mjd * u.d)
model = SkyModel(
spectral_model=spectral_model1,
temporal_model=temporal_model1,
name="model-test",
)
/Users/terrier/Code/anaconda3/envs/gammapy-dev/lib/python3.8/site-packages/astropy/units/quantity.py:613: RuntimeWarning: overflow encountered in exp
result = super().__array_ufunc__(function, method, *arrays, **kwargs)
/Users/terrier/Code/anaconda3/envs/gammapy-dev/lib/python3.8/site-packages/astropy/units/quantity.py:613: RuntimeWarning: invalid value encountered in subtract
result = super().__array_ufunc__(function, method, *arrays, **kwargs)
[18]:
datasets.models = model
[19]:
%%time
# Do a joint fit
fit = Fit()
result = fit.run(datasets=datasets)
CPU times: user 25.4 s, sys: 239 ms, total: 25.6 s
Wall time: 33.5 s
/Users/terrier/Code/anaconda3/envs/gammapy-dev/lib/python3.8/site-packages/astropy/units/quantity.py:613: RuntimeWarning: overflow encountered in exp
result = super().__array_ufunc__(function, method, *arrays, **kwargs)
/Users/terrier/Code/anaconda3/envs/gammapy-dev/lib/python3.8/site-packages/astropy/units/quantity.py:613: RuntimeWarning: invalid value encountered in subtract
result = super().__array_ufunc__(function, method, *arrays, **kwargs)
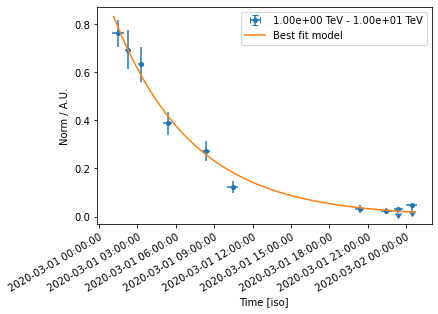
Now let’s plot model and data. We plot only the normalisation of the temporal model in relative units for one particular energy range
[20]:
lc_1TeV_10TeV = lc_1d.slice_by_idx({"energy": slice(2, 3)})
ax = lc_1TeV_10TeV.plot(sed_type="norm", axis_name="time")
time_range = lc_1TeV_10TeV.geom.axes["time"].time_bounds
temporal_model1.plot(ax=ax, time_range=time_range, label="Best fit model")
ax.set_yscale("linear")
plt.legend()
[20]:
<matplotlib.legend.Legend at 0x143f0b700>
Fit the datasets#
Here, we apply the models directly to the simulated datasets.
For modelling and fitting more complex flares, you should attach the relevant model to each group of datasets. The parameters of a model in a given group of dataset will be tied. For more details on joint fitting in gammapy, see here.
[21]:
# Define the model:
spectral_model2 = PowerLawSpectralModel(
index=2.0, amplitude="1e-12 cm-2 s-1 TeV-1", reference="1 TeV"
)
temporal_model2 = ExpDecayTemporalModel(t0="10 h", t_ref=gti_t0.mjd * u.d)
model2 = SkyModel(
spectral_model=spectral_model2,
temporal_model=temporal_model2,
name="model-test2",
)
/Users/terrier/Code/anaconda3/envs/gammapy-dev/lib/python3.8/site-packages/astropy/units/quantity.py:613: RuntimeWarning: overflow encountered in exp
result = super().__array_ufunc__(function, method, *arrays, **kwargs)
/Users/terrier/Code/anaconda3/envs/gammapy-dev/lib/python3.8/site-packages/astropy/units/quantity.py:613: RuntimeWarning: invalid value encountered in subtract
result = super().__array_ufunc__(function, method, *arrays, **kwargs)
[22]:
model2.parameters.to_table()
[22]:
| type | name | value | unit | error | min | max | frozen | is_norm | link |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| str8 | str9 | float64 | str14 | int64 | float64 | float64 | bool | bool | str1 |
| spectral | index | 2.0000e+00 | 0.000e+00 | nan | nan | False | False | ||
| spectral | amplitude | 1.0000e-12 | cm-2 s-1 TeV-1 | 0.000e+00 | nan | nan | False | True | |
| spectral | reference | 1.0000e+00 | TeV | 0.000e+00 | nan | nan | True | False | |
| temporal | t0 | 1.0000e+01 | h | 0.000e+00 | nan | nan | False | False | |
| temporal | t_ref | 5.8909e+04 | d | 0.000e+00 | nan | nan | True | False |
[23]:
datasets.models = model2
[24]:
%%time
# Do a joint fit
fit = Fit()
result = fit.run(datasets=datasets)
CPU times: user 21.5 s, sys: 82.6 ms, total: 21.5 s
Wall time: 23.2 s
/Users/terrier/Code/anaconda3/envs/gammapy-dev/lib/python3.8/site-packages/astropy/units/quantity.py:613: RuntimeWarning: overflow encountered in exp
result = super().__array_ufunc__(function, method, *arrays, **kwargs)
/Users/terrier/Code/anaconda3/envs/gammapy-dev/lib/python3.8/site-packages/astropy/units/quantity.py:613: RuntimeWarning: invalid value encountered in subtract
result = super().__array_ufunc__(function, method, *arrays, **kwargs)
[25]:
result.parameters.to_table()
[25]:
| type | name | value | unit | error | min | max | frozen | is_norm | link |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| str8 | str9 | float64 | str14 | float64 | float64 | float64 | bool | bool | str1 |
| spectral | index | 3.0232e+00 | 2.741e-02 | nan | nan | False | False | ||
| spectral | amplitude | 9.8974e-12 | cm-2 s-1 TeV-1 | 3.288e-13 | nan | nan | False | True | |
| spectral | reference | 1.0000e+00 | TeV | 0.000e+00 | nan | nan | True | False | |
| temporal | t0 | 6.1551e+00 | h | 2.199e-01 | nan | nan | False | False | |
| temporal | t_ref | 5.8909e+04 | d | 0.000e+00 | nan | nan | True | False |
We see that the fitted parameters are consistent between fitting flux points and datasets, and match well with the simulated ones
Exercises#
Re-do the analysis with
MapDatasetinstead ofSpectralDatasetModel the flare of PKS 2155-304 which you obtained using the light curve flare tutorial. Use a combination of a Gaussian and Exponential flare profiles, and fit using
scipy.optimize.curve_fitDo a joint fitting of the datasets.
