Note
Go to the end to download the full example code or to run this example in your browser via Binder
Pulsar analysis#
Produce a phasogram, phased-resolved maps and spectra in pulsar analysis.
Introduction#
This notebook shows how to do a pulsar analysis with Gammapy. It’s based on a Vela simulation file from the CTA DC1, which already contains a column of phases. We will produce a phasogram, a phase-resolved map and a phase-resolved spectrum of the Vela pulsar using the class PhaseBackgroundEstimator.
The phasing in itself is not done here, and it requires specific packages like Tempo2 or PINT.
Opening the data#
Let’s first do the imports and load the only observation containing Vela in the CTA 1DC dataset shipped with Gammapy.
import numpy as np
import astropy.units as u
from astropy.coordinates import SkyCoord
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# %matplotlib inline
from IPython.display import display
from gammapy.data import DataStore
from gammapy.datasets import Datasets, FluxPointsDataset, SpectrumDataset
from gammapy.estimators import FluxPointsEstimator
from gammapy.makers import PhaseBackgroundMaker, SafeMaskMaker, SpectrumDatasetMaker
from gammapy.maps import Map, MapAxis, RegionGeom, WcsGeom
from gammapy.modeling import Fit
from gammapy.modeling.models import PowerLawSpectralModel, SkyModel
Check setup#
from gammapy.utils.check import check_tutorials_setup
from gammapy.utils.regions import SphericalCircleSkyRegion
check_tutorials_setup()
System:
python_executable : /home/runner/work/gammapy-docs/gammapy-docs/gammapy/.tox/build_docs/bin/python
python_version : 3.9.16
machine : x86_64
system : Linux
Gammapy package:
version : 1.0.1
path : /home/runner/work/gammapy-docs/gammapy-docs/gammapy/.tox/build_docs/lib/python3.9/site-packages/gammapy
Other packages:
numpy : 1.24.2
scipy : 1.10.1
astropy : 5.2.1
regions : 0.7
click : 8.1.3
yaml : 6.0
IPython : 8.11.0
jupyterlab : not installed
matplotlib : 3.7.1
pandas : not installed
healpy : 1.16.2
iminuit : 2.21.0
sherpa : 4.15.0
naima : 0.10.0
emcee : 3.1.4
corner : 2.2.1
Gammapy environment variables:
GAMMAPY_DATA : /home/runner/work/gammapy-docs/gammapy-docs/gammapy-datasets/1.0.1
Load the data store (which is a subset of CTA-DC1 data):
data_store = DataStore.from_dir("$GAMMAPY_DATA/cta-1dc/index/gps")
Define obsevation ID and print events:
id_obs_vela = [111630]
obs_list_vela = data_store.get_observations(id_obs_vela)
print(obs_list_vela[0].events)
EventList
---------
Instrument : None
Telescope : CTA
Obs. ID : 111630
Number of events : 101430
Event rate : 56.350 1 / s
Time start : 59300.833333333336
Time stop : 59300.854166666664
Min. energy : 3.00e-02 TeV
Max. energy : 1.52e+02 TeV
Median energy : 1.00e-01 TeV
Max. offset : 5.0 deg
Now that we have our observation, let’s select the events in 0.2° radius around the pulsar position.
pos_target = SkyCoord(ra=128.836 * u.deg, dec=-45.176 * u.deg, frame="icrs")
on_radius = 0.2 * u.deg
on_region = SphericalCircleSkyRegion(pos_target, on_radius)
# Apply angular selection
events_vela = obs_list_vela[0].events.select_region(on_region)
print(events_vela)
EventList
---------
Instrument : None
Telescope : CTA
Obs. ID : 111630
Number of events : 843
Event rate : 0.468 1 / s
Time start : 59300.833333333336
Time stop : 59300.854166666664
Min. energy : 3.00e-02 TeV
Max. energy : 4.33e+01 TeV
Median energy : 1.07e-01 TeV
Max. offset : 1.7 deg
Let’s load the phases of the selected events in a dedicated array.
phases = events_vela.table["PHASE"]
# Let's take a look at the first 10 phases
display(phases[:10])
PHASE
-----------
0.81847286
0.45646095
0.111507416
0.43416595
0.76837444
0.3639946
0.58693695
0.51095676
0.5606985
0.2505703
Phasogram#
Once we have the phases, we can make a phasogram. A phasogram is a histogram of phases and it works exactly like any other histogram (you can set the binning, evaluate the errors based on the counts in each bin, etc).
nbins = 30
phase_min, phase_max = (0, 1)
values, bin_edges = np.histogram(phases, range=(phase_min, phase_max), bins=nbins)
bin_width = (phase_max - phase_min) / nbins
bin_center = (bin_edges[:-1] + bin_edges[1:]) / 2
# Poissonian uncertainty on each bin
values_err = np.sqrt(values)
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.bar(
x=bin_center,
height=values,
width=bin_width,
color="#d53d12",
alpha=0.8,
edgecolor="black",
yerr=values_err,
)
ax.set_xlim(0, 1)
ax.set_xlabel("Phase")
ax.set_ylabel("Counts")
ax.set_title(f"Phasogram with angular cut of {on_radius}")
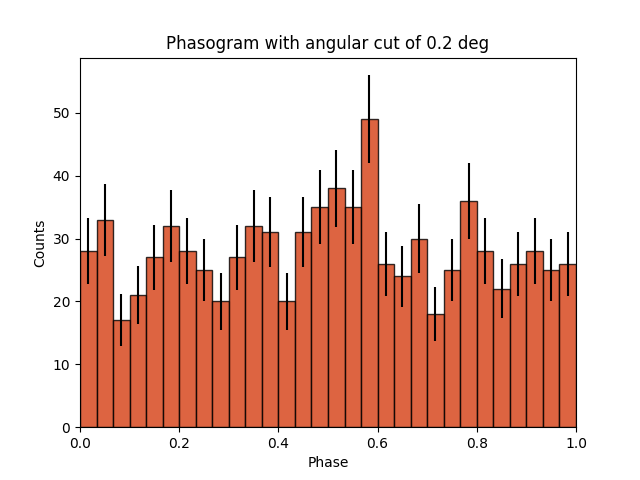
Text(0.5, 1.0, 'Phasogram with angular cut of 0.2 deg')
Now let’s add some fancy additions to our phasogram: a patch on the ON- and OFF-phase regions and one for the background level.
# Evaluate background level
off_phase_range = (0.7, 1.0)
on_phase_range = (0.5, 0.6)
mask_off = (off_phase_range[0] < phases) & (phases < off_phase_range[1])
count_bkg = mask_off.sum()
print(f"Number of Off events: {count_bkg}")
# bkg level normalized by the size of the OFF zone (0.3)
bkg = count_bkg / nbins / (off_phase_range[1] - off_phase_range[0])
# error on the background estimation
bkg_err = np.sqrt(count_bkg) / nbins / (off_phase_range[1] - off_phase_range[0])
# Let's redo the same plot for the basis
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.bar(
x=bin_center,
height=values,
width=bin_width,
color="#d53d12",
alpha=0.8,
edgecolor="black",
yerr=values_err,
)
# Plot background level
x_bkg = np.linspace(0, 1, 50)
kwargs = {"color": "black", "alpha": 0.5, "ls": "--", "lw": 2}
ax.plot(x_bkg, (bkg - bkg_err) * np.ones_like(x_bkg), **kwargs)
ax.plot(x_bkg, (bkg + bkg_err) * np.ones_like(x_bkg), **kwargs)
ax.fill_between(
x_bkg, bkg - bkg_err, bkg + bkg_err, facecolor="grey", alpha=0.5
) # grey area for the background level
# Let's make patches for the on and off phase zones
on_patch = ax.axvspan(
on_phase_range[0], on_phase_range[1], alpha=0.3, color="gray", ec="black"
)
off_patch = ax.axvspan(
off_phase_range[0],
off_phase_range[1],
alpha=0.4,
color="white",
hatch="x",
ec="black",
)
# Legends "ON" and "OFF"
ax.text(0.55, 5, "ON", color="black", fontsize=17, ha="center")
ax.text(0.895, 5, "OFF", color="black", fontsize=17, ha="center")
ax.set_xlabel("Phase")
ax.set_ylabel("Counts")
ax.set_xlim(0, 1)
ax.set_title(f"Phasogram with angular cut of {on_radius}")
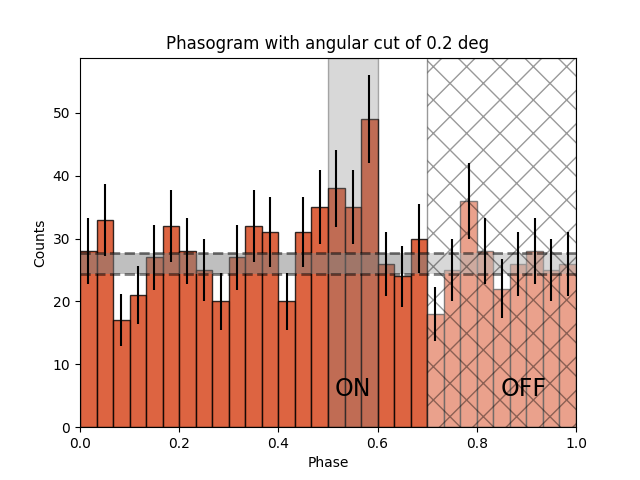
Number of Off events: 234
Text(0.5, 1.0, 'Phasogram with angular cut of 0.2 deg')
Phase-resolved map#
Now that the phases are computed, we want to do a phase-resolved sky map : a map of the ON-phase events minus alpha times the OFF-phase events. Alpha is the ratio between the size of the ON-phase zone (here 0.1) and the OFF-phase zone (0.3). It’s a map of the excess events in phase, which are the pulsed events.
geom = WcsGeom.create(binsz=0.02 * u.deg, skydir=pos_target, width="5 deg")
Let’s create an ON-map and an OFF-map:
on_map = Map.from_geom(geom)
off_map = Map.from_geom(geom)
events_vela_on = events_vela.select_parameter("PHASE", on_phase_range)
events_vela_off = events_vela.select_parameter("PHASE", off_phase_range)
on_map.fill_events(events_vela_on)
off_map.fill_events(events_vela_off)
# Defining alpha as the ratio of the ON and OFF phase zones
alpha = (on_phase_range[1] - on_phase_range[0]) / (
off_phase_range[1] - off_phase_range[0]
)
# Create and fill excess map
# The pulsed events are the difference between the ON-phase count and alpha times the OFF-phase count
excess_map = on_map - off_map * alpha
# Plot excess map
plt.figure()
excess_map.smooth(kernel="gauss", width=0.2 * u.deg).plot(add_cbar=True)
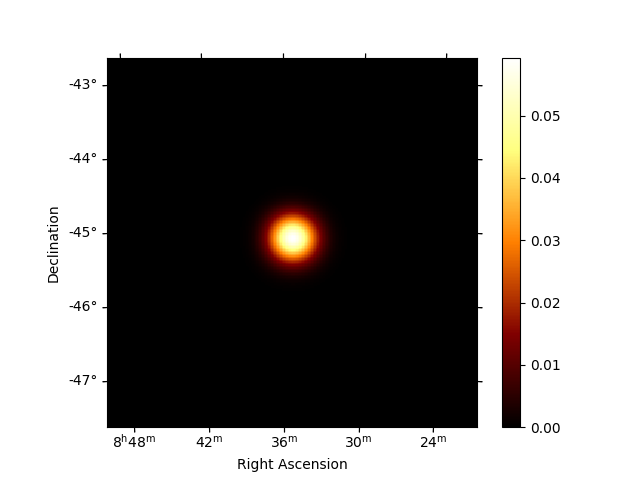
<WCSAxes: >
Phase-resolved spectrum#
We can also do a phase-resolved spectrum. In order to do that, there is the class PhaseBackgroundMaker. In a phase-resolved analysis, the background is estimated in the same sky region but in the OFF-phase zone.
e_true = MapAxis.from_energy_bounds(0.003, 10, 100, unit="TeV", name="energy_true")
e_reco = MapAxis.from_energy_bounds(0.01, 10, 30, unit="TeV", name="energy")
geom = RegionGeom.create(region=on_region, axes=[e_reco])
dataset_empty = SpectrumDataset.create(geom=geom, energy_axis_true=e_true)
dataset_maker = SpectrumDatasetMaker()
phase_bkg_maker = PhaseBackgroundMaker(
on_phase=on_phase_range, off_phase=off_phase_range
)
safe_mask_maker = SafeMaskMaker(methods=["aeff-default", "edisp-bias"], bias_percent=20)
datasets = []
for obs in obs_list_vela:
dataset = dataset_maker.run(dataset_empty, obs)
dataset_on_off = phase_bkg_maker.run(dataset, obs)
dataset_on_off = safe_mask_maker.run(dataset_on_off, obs)
datasets.append(dataset_on_off)
/home/runner/work/gammapy-docs/gammapy-docs/gammapy/.tox/build_docs/lib/python3.9/site-packages/gammapy/maps/geom.py:48: RuntimeWarning: invalid value encountered in cast
p_idx = np.rint(p).astype(int)
/home/runner/work/gammapy-docs/gammapy-docs/gammapy/.tox/build_docs/lib/python3.9/site-packages/astropy/units/core.py:2097: UnitsWarning: '1/s/MeV/sr' did not parse as fits unit: Numeric factor not supported by FITS If this is meant to be a custom unit, define it with 'u.def_unit'. To have it recognized inside a file reader or other code, enable it with 'u.add_enabled_units'. For details, see https://docs.astropy.org/en/latest/units/combining_and_defining.html
warnings.warn(msg, UnitsWarning)
/home/runner/work/gammapy-docs/gammapy-docs/gammapy/.tox/build_docs/lib/python3.9/site-packages/gammapy/maps/geom.py:48: RuntimeWarning: invalid value encountered in cast
p_idx = np.rint(p).astype(int)
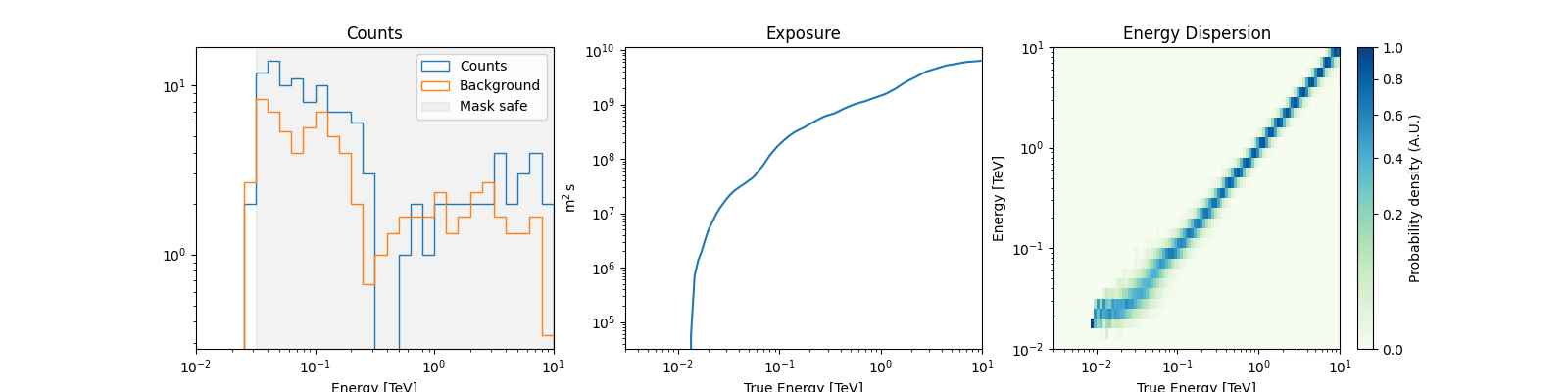
Now let’s a look at the datasets we just created:
datasets[0].peek()
Now we’ll fit a model to the spectrum with the Fit class. First we
load a power law model with an initial value for the index and the
amplitude and then wo do a likelihood fit. The fit results are printed
below.
spectral_model = PowerLawSpectralModel(
index=4, amplitude="1.3e-9 cm-2 s-1 TeV-1", reference="0.02 TeV"
)
model = SkyModel(spectral_model=spectral_model, name="vela psr")
emin_fit, emax_fit = (0.04 * u.TeV, 0.4 * u.TeV)
mask_fit = geom.energy_mask(energy_min=emin_fit, energy_max=emax_fit)
for dataset in datasets:
dataset.models = model
dataset.mask_fit = mask_fit
joint_fit = Fit()
joint_result = joint_fit.run(datasets=datasets)
print(joint_result)
OptimizeResult
backend : minuit
method : migrad
success : True
message : Optimization terminated successfully.
nfev : 101
total stat : 7.07
CovarianceResult
backend : minuit
method : hesse
success : True
message : Hesse terminated successfully.
Now you might want to do the stacking here even if in our case there is only one observation which makes it superfluous. We can compute flux points by fitting the norm of the global model in energy bands.
energy_edges = np.logspace(np.log10(0.04), np.log10(0.4), 7) * u.TeV
dataset = Datasets(datasets).stack_reduce()
dataset.models = model
fpe = FluxPointsEstimator(
energy_edges=energy_edges, source="vela psr", selection_optional="all"
)
flux_points = fpe.run(datasets=[dataset])
flux_points.meta["ts_threshold_ul"] = 1
amplitude_ref = 0.57 * 19.4e-14 * u.Unit("1 / (cm2 s MeV)")
spec_model_true = PowerLawSpectralModel(
index=4.5, amplitude=amplitude_ref, reference="20 GeV"
)
flux_points_dataset = FluxPointsDataset(data=flux_points, models=model)
Now we can plot.
ax_spectrum, ax_residuals = flux_points_dataset.plot_fit()
ax_spectrum.set_ylim([1e-14, 3e-11])
ax_residuals.set_ylim([-1.7, 1.7])
spec_model_true.plot(
ax=ax_spectrum,
energy_bounds=(emin_fit, emax_fit),
label="Reference model",
c="black",
linestyle="dashed",
energy_power=2,
)
ax_spectrum.legend(loc="best")
plt.show()
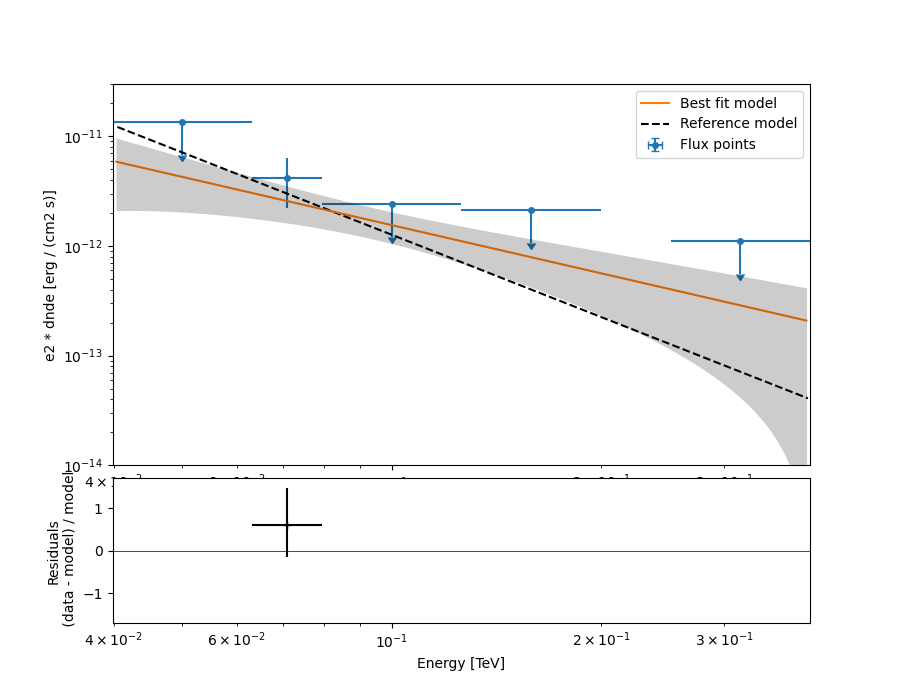
This tutorial suffers a bit from the lack of statistics: there were 9 Vela observations in the CTA DC1 while there is only one here. When done on the 9 observations, the spectral analysis is much better agreement between the input model and the gammapy fit.