This is a fixed-text formatted version of a Jupyter notebook
- Try online
- You can contribute with your own notebooks in this GitHub repository.
- Source files: image_analysis.ipynb | image_analysis.py
Fitting 2D images with Gammapy¶
Gammapy does not have any special handling for 2D images, but treats them as a subset of maps. Thus, classical 2D image analysis can be done in 2 independent ways:
- Using the sherpa pacakge, see: image_fitting_with_sherpa.ipynb,
- Within gammapy, by assuming 2D analysis to be a sub-set of the generalised
maps. Thus, analysis should proceeexactly as demonstrated in analysis_3d.ipynb, taking care of a few things that we mention in this tutorial
We consider 2D images to be a special case of 3D maps, ie, maps with only one energy bin. This is a major difference while analysing in sherpa, where the maps must not contain any energy axis. In this tutorial, we do a classical image analysis using three example observations of the Galactic center region with CTA - i.e., study the source flux and morphology.
Setup¶
[1]:
%matplotlib inline
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from scipy.stats import norm
import astropy.units as u
from astropy.coordinates import SkyCoord
from astropy.convolution import Tophat2DKernel
from regions import CircleSkyRegion
from gammapy.detect import compute_lima_on_off_image
from gammapy.data import DataStore
from gammapy.irf import make_mean_psf
from gammapy.maps import Map, MapAxis, WcsGeom
from gammapy.cube import (
MapMaker,
PSFKernel,
MapDataset,
MapMakerRing,
RingBackgroundEstimator,
)
from gammapy.modeling.models import (
SkyModel,
BackgroundModel,
PowerLaw2SpectralModel,
PointSpatialModel,
)
from gammapy.modeling import Fit
Prepare modeling input data¶
The counts, exposure and the background maps¶
This is the same drill - use DataStore object to access the CTA observations and retrieve a list of observations by passing the observations IDs to the .get_observations() method, then use MapMaker to make the maps.
[2]:
# Define which data to use and print some information
data_store = DataStore.from_dir("$GAMMAPY_DATA/cta-1dc/index/gps/")
data_store.info()
Data store:
HDU index table:
BASE_DIR: /Users/adonath/data/gammapy-data/cta-1dc/index/gps
Rows: 24
OBS_ID: 110380 -- 111630
HDU_TYPE: ['aeff', 'bkg', 'edisp', 'events', 'gti', 'psf']
HDU_CLASS: ['aeff_2d', 'bkg_3d', 'edisp_2d', 'events', 'gti', 'psf_3gauss']
Observation table:
Observatory name: 'N/A'
Number of observations: 4
[3]:
data_store.obs_table["ONTIME"].quantity.sum().to("hour")
[3]:
[4]:
# Select some observations from these dataset by hand
obs_ids = [110380, 111140, 111159]
observations = data_store.get_observations(obs_ids)
[5]:
emin, emax = [0.1, 10] * u.TeV
energy_axis = MapAxis.from_bounds(
emin.value, emax.value, 10, unit="TeV", name="energy", interp="log"
)
geom = WcsGeom.create(
skydir=(0, 0),
binsz=0.02,
width=(10, 8),
coordsys="GAL",
proj="CAR",
axes=[energy_axis],
)
Note that even when doing a 2D analysis, it is better to use fine energy bins in the beginning and then sum them over. This is to ensure that the background shape can be approximated by a power law function in each energy bin. The run_images() can be used to compute maps in fine bins and then squash them to have one bin. This can be done by specifying keep_dims = True. This will compute a summed counts and background maps, and a spectral weighted exposure map.
[6]:
%%time
maker = MapMaker(geom, offset_max=4.0 * u.deg)
spectrum = PowerLaw2SpectralModel(index=2)
maps2D = maker.run_images(observations, spectrum=spectrum, keepdims=True)
WARNING: Tried to get polar motions for times after IERS data is valid. Defaulting to polar motion from the 50-yr mean for those. This may affect precision at the 10s of arcsec level [astropy.coordinates.builtin_frames.utils]
/Users/adonath/github/adonath/gammapy/gammapy/utils/interpolation.py:159: Warning: Interpolated values reached float32 precision limit
"Interpolated values reached float32 precision limit", Warning
CPU times: user 15.7 s, sys: 3.23 s, total: 18.9 s
Wall time: 19.6 s
For a typical 2D analysis, using an energy dispersion usually does not make sense. A PSF map can be made as in the regular 3D case, taking care to weight it properly with the spectrum.
[7]:
# mean PSF
geom2d = maps2D["exposure"].geom
src_pos = SkyCoord(0, 0, unit="deg", frame="galactic")
table_psf = make_mean_psf(observations, src_pos)
table_psf_2d = table_psf.table_psf_in_energy_band(
(emin, emax), spectrum=spectrum
)
# PSF kernel used for the model convolution
psf_kernel = PSFKernel.from_table_psf(
table_psf_2d, geom2d, max_radius="0.3 deg"
)
Now, the analysis proceeds as usual. Just take care to use the proper geometry in this case.
Define a mask¶
[8]:
region = CircleSkyRegion(center=src_pos, radius=0.6 * u.deg)
mask = geom2d.region_mask([region])
Modeling the source¶
This is the important thing to note in this analysis. Since modeling and fitting in gammapy.maps needs to have a combination of spectral models, we have to use a dummy Powerlaw as for the spectral model and fix its index to 2. Since we are interested only in the integral flux, we will use the PowerLaw2SpectralModel model which directly fits an integral flux.
[9]:
spatial_model = PointSpatialModel(
lon_0="0.01 deg", lat_0="0.01 deg", frame="galactic"
)
spectral_model = PowerLaw2SpectralModel(
emin=emin, emax=emax, index=2.0, amplitude="3e-12 cm-2 s-1"
)
model = SkyModel(spatial_model=spatial_model, spectral_model=spectral_model)
model.parameters["index"].frozen = True
Modeling the background¶
Gammapy fitting framework assumes the background to be an integrated model. Thus, we will define the background as a model, and freeze its parameters for now.
[10]:
background_model = BackgroundModel(maps2D["background"])
background_model.parameters["norm"].frozen = True
background_model.parameters["tilt"].frozen = True
[11]:
dataset = MapDataset(
model=model,
counts=maps2D["counts"],
exposure=maps2D["exposure"],
background_model=background_model,
mask_fit=mask,
psf=psf_kernel,
)
[12]:
%%time
fit = Fit(dataset)
result = fit.run()
CPU times: user 1.05 s, sys: 20.5 ms, total: 1.07 s
Wall time: 1.14 s
To see the actual best-fit parameters, do a print on the result
[13]:
print(model)
SkyModel
Parameters:
name value error unit min max frozen
--------- ---------- ----- -------- ---------- --------- ------
lon_0 -5.364e-02 nan deg nan nan False
lat_0 -5.058e-02 nan deg -9.000e+01 9.000e+01 False
index 2.000e+00 nan nan nan True
amplitude 4.292e-11 nan cm-2 s-1 nan nan False
emin 1.000e-01 nan TeV nan nan True
emax 1.000e+01 nan TeV nan nan True
[14]:
# To get the errors on the model, we can check the covariance table:
result.parameters.covariance_to_table()
[14]:
| name | lon_0 | lat_0 | index | amplitude | emin | emax | norm | tilt | reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| str9 | float64 | float64 | float64 | float64 | float64 | float64 | float64 | float64 | float64 |
| lon_0 | 1.083e-05 | 5.277e-07 | 0.000e+00 | -4.312e-16 | 0.000e+00 | 0.000e+00 | 0.000e+00 | 0.000e+00 | 0.000e+00 |
| lat_0 | 5.277e-07 | 1.099e-05 | 0.000e+00 | -3.271e-16 | 0.000e+00 | 0.000e+00 | 0.000e+00 | 0.000e+00 | 0.000e+00 |
| index | 0.000e+00 | 0.000e+00 | 0.000e+00 | 0.000e+00 | 0.000e+00 | 0.000e+00 | 0.000e+00 | 0.000e+00 | 0.000e+00 |
| amplitude | -4.312e-16 | -3.271e-16 | 0.000e+00 | 3.282e-24 | 0.000e+00 | 0.000e+00 | 0.000e+00 | 0.000e+00 | 0.000e+00 |
| emin | 0.000e+00 | 0.000e+00 | 0.000e+00 | 0.000e+00 | 0.000e+00 | 0.000e+00 | 0.000e+00 | 0.000e+00 | 0.000e+00 |
| emax | 0.000e+00 | 0.000e+00 | 0.000e+00 | 0.000e+00 | 0.000e+00 | 0.000e+00 | 0.000e+00 | 0.000e+00 | 0.000e+00 |
| norm | 0.000e+00 | 0.000e+00 | 0.000e+00 | 0.000e+00 | 0.000e+00 | 0.000e+00 | 0.000e+00 | 0.000e+00 | 0.000e+00 |
| tilt | 0.000e+00 | 0.000e+00 | 0.000e+00 | 0.000e+00 | 0.000e+00 | 0.000e+00 | 0.000e+00 | 0.000e+00 | 0.000e+00 |
| reference | 0.000e+00 | 0.000e+00 | 0.000e+00 | 0.000e+00 | 0.000e+00 | 0.000e+00 | 0.000e+00 | 0.000e+00 | 0.000e+00 |
Classical Ring Background Analysis¶
No we repeat the same analyis but useing a classical ring background estimation. This is currently support with a separate MapMakerRing. However We start by defining an exclusion mask:
[15]:
geom_image = geom.to_image()
regions = CircleSkyRegion(center=spatial_model.position, radius=0.3 * u.deg)
exclusion_mask = Map.from_geom(geom_image)
exclusion_mask.data = geom_image.region_mask([regions], inside=False)
exclusion_mask.plot();
Next we define the parameters of the ring background and create the RingBackgroundEstimator:
[16]:
ring_bkg = RingBackgroundEstimator(r_in="0.3 deg", width="0.3 deg")
[17]:
%%time
im = MapMakerRing(
geom=geom,
offset_max=3.0 * u.deg,
exclusion_mask=exclusion_mask,
background_estimator=ring_bkg,
)
for obs in observations:
im._get_obs_maker(obs)
images = im.run_images(observations)
WARNING: Tried to get polar motions for times after IERS data is valid. Defaulting to polar motion from the 50-yr mean for those. This may affect precision at the 10s of arcsec level [astropy.coordinates.builtin_frames.utils]
CPU times: user 7.33 s, sys: 1.37 s, total: 8.7 s
Wall time: 12.6 s
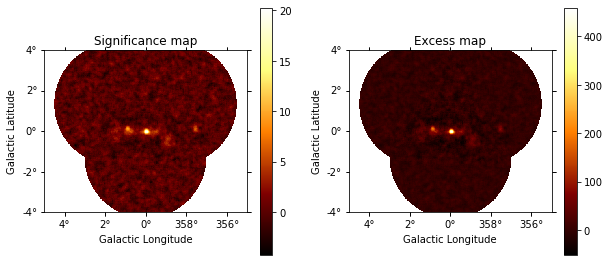
Based on the estimate of the ring background we compute a Li&Ma significance image:
[18]:
scale = geom.pixel_scales[0].to("deg")
# Using a convolution radius of 0.05 degrees
theta = 0.1 * u.deg / scale
tophat = Tophat2DKernel(theta)
tophat.normalize("peak")
lima_maps = compute_lima_on_off_image(
images["on"],
images["off"],
images["exposure_on"],
images["exposure_off"],
tophat,
)
[19]:
significance_map = lima_maps["significance"]
excess_map = lima_maps["excess"]
That is what the excess and significance look like:
[20]:
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))
ax1 = plt.subplot(221, projection=significance_map.geom.wcs)
ax2 = plt.subplot(222, projection=excess_map.geom.wcs)
ax1.set_title("Significance map")
significance_map.plot(ax=ax1, add_cbar=True)
ax2.set_title("Excess map")
excess_map.plot(ax=ax2, add_cbar=True);
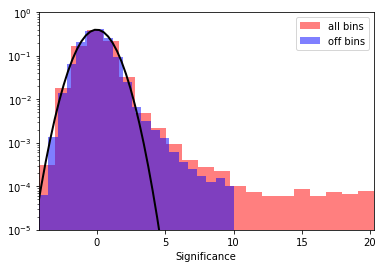
Finally we take a look at the signficance distribution outside the exclusion region:
[21]:
# create a 2D mask for the images
significance_map_off = significance_map * exclusion_mask
[22]:
significance_all = significance_map.data[np.isfinite(significance_map.data)]
significance_off = significance_map_off.data[
np.isfinite(significance_map_off.data)
]
plt.hist(
significance_all,
density=True,
alpha=0.5,
color="red",
label="all bins",
bins=21,
)
plt.hist(
significance_off,
density=True,
alpha=0.5,
color="blue",
label="off bins",
bins=21,
)
# Now, fit the off distribution with a Gaussian
mu, std = norm.fit(significance_off)
x = np.linspace(-8, 8, 50)
p = norm.pdf(x, mu, std)
plt.plot(x, p, lw=2, color="black")
plt.legend()
plt.xlabel("Significance")
plt.yscale("log")
plt.ylim(1e-5, 1)
xmin, xmax = np.min(significance_all), np.max(significance_all)
plt.xlim(xmin, xmax)
print("Fit results: mu = {:.2f}, std = {:.2f}".format(mu, std))
Fit results: mu = -0.03, std = 1.00
Exercises¶
- Update the exclusion mask in the ring background example by thresholding the significance map and re-run the background estimator
- Plot residual maps as done in the
analysis_3dnotebook - Iteratively add and fit sources as explained in
image_fitting_with_sherpanotebook
[ ]: