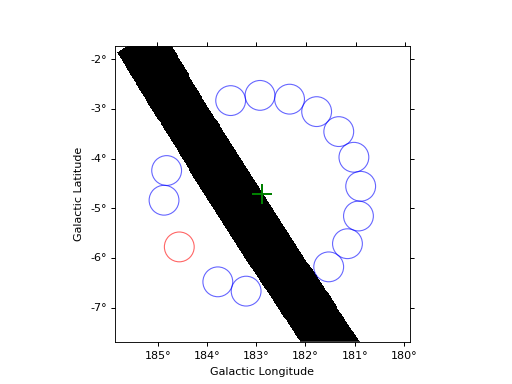
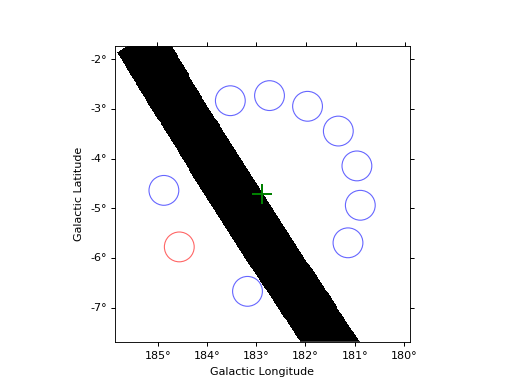
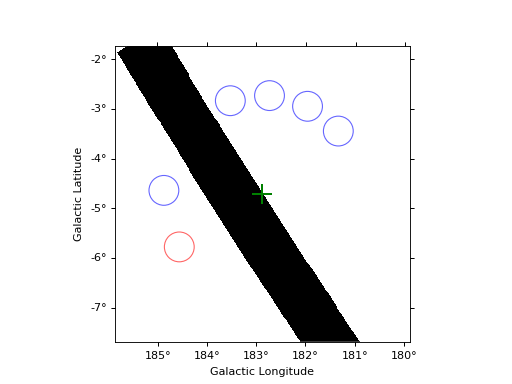
Reflected regions¶
Details on the reflected regions method can be found in [Berge2007]
The following example illustrates how to create reflected regions for a given
circular on region and exclusion mask using the ReflectedRegionsFinder.
"""Example how to compute and plot reflected regions."""
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from astropy.coordinates import SkyCoord, Angle
from regions import CircleSkyRegion
from gammapy.maps import WcsNDMap
from gammapy.background import ReflectedRegionsFinder
# Exclude a rectangular region
exclusion_mask = WcsNDMap.create(npix=(801, 701), binsz=0.01, skydir=(83.6, 23.0))
coords = exclusion_mask.geom.get_coord().skycoord
mask = (Angle("23d") < coords.dec) & (coords.dec < Angle("24d"))
exclusion_mask.data = np.invert(mask)
pos = SkyCoord(83.633, 22.014, unit="deg")
radius = Angle(0.3, "deg")
on_region = CircleSkyRegion(pos, radius)
center = SkyCoord(83.633, 24, unit="deg")
# One can impose a minimal distance between ON region and first reflected regions
finder = ReflectedRegionsFinder(
region=on_region,
center=center,
exclusion_mask=exclusion_mask,
min_distance_input="0.2 rad",
)
finder.run()
fig1 = plt.figure(1)
finder.plot(fig=fig1)
# One can impose a minimal distance between two adjacent regions
finder = ReflectedRegionsFinder(
region=on_region,
center=center,
exclusion_mask=exclusion_mask,
min_distance_input="0.2 rad",
min_distance="0.1 rad",
)
finder.run()
fig2 = plt.figure(2)
finder.plot(fig=fig2)
# One can impose a maximal number of regions to be extracted
finder = ReflectedRegionsFinder(
region=on_region,
center=center,
exclusion_mask=exclusion_mask,
min_distance_input="0.2 rad",
max_region_number=5,
min_distance="0.1 rad",
)
finder.run()
fig3 = plt.figure(3)
finder.plot(fig=fig3)
plt.show()