Dark matter#
Introduction#
The gammapy.astro.darkmatter module provides spatial and spectral models for
indirect dark matter searches, using PPPC4DM models. This introduction is aimed
at people who already have some experience with dark matter analysis. For a thorough
introduction see e.g. Cirelli 2014.
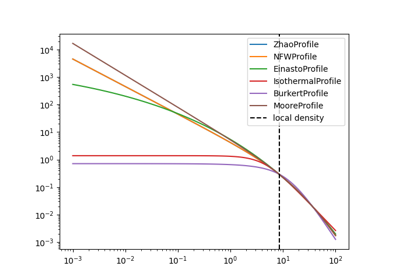
The spatial distribution of dark matter halos is typically modeled with
radially symmetric profiles. Common profiles are the ones by Navarro, Frenk and
White (NFW) or Einasto for cuspy and an Isothermal or Burkert profile for cored
dark matter distributions (see gammapy.astro.darkmatter.DMProfile).
The spectral models in gammapy.astro.darkmatter.PrimaryFlux are based on
Cirelli et al. 2011, who provide tabulated spectra for different
annihilation channels). These models are most commonly used in VHE dark matter
analyses.
Other packages#
There are many other packages out there that implement functionality for dark matter analysis, their capabilities are summarized in the following
FermiST#
The Fermi Science tools have a DMFitFunction with the following XML serialization format
<source name="DM_Example" type="PointSource">
<spectrum file="$(BASE_DIR)/data/Likelihood/gammamc_dif.dat" type="DMFitFunction">
<parameter error="1." free="0" max="1.e+5" min="1.e-5" name="norm" scale="1.e+20" value="5.0" />
<parameter error="1." free="0" max="5000.0" min="0." name="sigmav" scale="1.e-26" value="3.0" />
<parameter error="1." free="0" max="5000.0" min="1." name="mass" scale="1.0" value="10"/>
<parameter error="0.1" free="0" max="1.0" min="0.0" name="bratio" scale="1.0" value="1"/>
<parameter free="0" max="10" min="1" name="channel0" scale="1.0" value="4"/> <parameter free="0" max="10" min="1" name="channel1" scale="1.0" value="1"/>
</spectrum>
<spatialModel type="SkyDirFunction">
<parameter free="0" max="360" min="-360" name="RA" scale="1.0" value="128.8272"/>
<parameter free="0" max="90" min="-90" name="DEC" scale="1.0" value="-45.1762"/>
</spatialModel>
</source>
The DMFitFunction is only a spectral model and the spatial component is set using a point source. A spatial template can obviously be used. Utilities to create such sky maps are for example fermipy/dmsky but it seems like this package is basically a collection of spatial models from the literature. There is also fermiPy/dmpipe but it also does not seem to implement any spatial profiles.
The DMFitFunction is also implemented in fermipy.spectrum.DMFitFunction. It is a spectral model based on Jeltema & Profuma 2008. From a quick look I didn’t see where they get the spectral template from (obviously not Cirelli et al. 2011) but DarkSUSY is mentioned in the paper.
DMFitFunction is also implemented in astromodels.
None of the mentioned packages implement the spectral models by Cirelli et al. 2011
CLUMPY#
CLUMPY is a package for γ-ray signals from dark matter structures. The core of the code is the calculation of the line of sight integral of the dark matter density squared (for annihilations) or density (for decaying dark matter). CLUMPY is written in C/C++ and relies on the CERN ROOT library. There is no Python wrapper, as far as I can see. The available dark matter profiles go beyond what is used in usual VHE analyses. It might be worth looking into this package for cross checking the functionality in gammapy.
gamLike#
GamLike contains likelihood functions for most leading gamma-ray indirect searches for dark matter, including Fermi-LAT observations of dwarfs and the Galactic Centre (GC), HESS observations of the GC, and projected sensitivities for CTAO observations of the GC. It is released in tandem with the GAMBIT module DarkBit. DarkBit can be used for directly computing observables and likelihoods, for any combination of parameter values in some underlying particle model.