Tutorials#
Important
It is strongly advised to first read Fundamental Concepts: Gammapy analysis workflow and package structure of the User Guide before using the tutorials.
In general, all methods and classes are defined with default values that permit a good execution per default. In the tutorials, we frequently use extra values to just illustrate their usage.
The Gammapy library is used by many instruments and as consequence can not describe the specificities of each data release of each observatory. Get in touch with the observatory experts to get the best usage of a given data release.
This page lists the Gammapy tutorials that are available as Jupyter notebooks. You can read them here, or execute them using a temporary cloud server in Binder.
To execute them locally, you have to first install Gammapy locally (see
Installation) and download the tutorial notebooks and example datasets (see
Getting started). Once Gammapy is installed, remember that you can always
use gammapy tutorial setup to check your tutorial setup, or in your script with
from gammapy.utils.check import check_tutorials_setup
check_tutorials_setup()
Gammapy is a Python package built on Numpy and Astropy, so to use it effectively, you have to learn the basics. Many good free resources are available, e.g. A Whirlwind tour of Python, the Python data science handbook and the Astropy Hands-On Tutorial.
Introduction#
The following three tutorials show different ways of how to use Gammapy to perform a complete data analysis, from data selection to data reduction and finally modeling and fitting.
The first tutorial is an overview on how to perform a standard analysis workflow using the high level interface in a configuration-driven approach, whilst the second deals with the same use-case using the low level API and showing what is happening under-the-hood. The third tutorial shows a glimpse of how to handle different basic data structures like event lists, source catalogs, sky maps, spectral models and flux points tables.
Data exploration#
These tutorials show how to perform data exploration with Gammapy, providing an introduction to H.E.S.S., MAGIC, VERITAS, CTAO, HAWC and Fermi-LAT data and their instrument response functions (IRFs). You will learn to explore and filter event lists according to different criteria, view multidimensional IRF files and perform instrument-specific analysis.
Model Gallery#
A gallery of all possible spectral, spatial and temporal models can be found in this page: Model gallery.
Detailed explanation#
The following tutorials demonstrate different how to use Gammapy tools across the full analysis chain, from data loading to model comparison.
Data analysis#
The following set of tutorials are devoted to data analysis, and grouped according to the specific covered use cases in spectral analysis and flux fitting, image and cube analysis modelling and fitting, as well as time-dependent analysis with light-curves.
1D Spectral#
2D Image#
3D Cube#
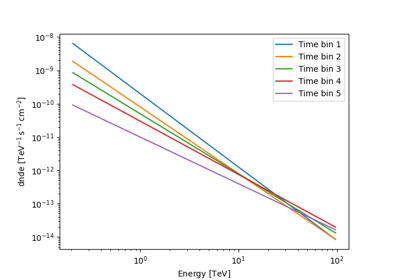
Sample a source with energy-dependent temporal evolution
Time series#
Astrophysics use cases#
This section outlines some source specific use cases.
Scripts#
For interactive use, IPython and Jupyter are great, and most Gammapy examples use those. However, for long-running, non-interactive tasks like data reduction or survey maps, you might prefer a Python script.
The following example shows how to run Gammapy within a Python script.