GaussianSpatialModel¶
-
class
gammapy.modeling.models.GaussianSpatialModel(lon_0, lat_0, sigma, e=0, phi='0 deg', frame='icrs')[source]¶ Bases:
gammapy.modeling.models.SpatialModelTwo-dimensional Gaussian model.
By default, the Gaussian is symmetric:
\[\phi(\text{lon}, \text{lat}) = N \times \exp\left\{-\frac{1}{2} \frac{1-\cos \theta}{1-\cos \sigma}\right\}\,,\]where \(\theta\) is the sky separation to the model center. In this case, the Gaussian is normalized to 1 on the sphere:
\[N = \frac{1}{4\pi a\left[1-\exp(-1/a)\right]}\,,\,\,\,\, a = 1-\cos \sigma\,.\]In the limit of small \(\theta\) and \(\sigma\), this definition reduces to the usual form:
\[\phi(\text{lon}, \text{lat}) = \frac{1}{2\pi\sigma^2} \exp{\left(-\frac{1}{2} \frac{\theta^2}{\sigma^2}\right)}\,.\]In case an eccentricity (\(e\)) and rotation angle (\(\phi\)) are passed, then the model is an elongated Gaussian, whose evaluation is performed as in the symmetric case but using the effective radius of the Gaussian:
\[\sigma_{eff}(\text{lon}, \text{lat}) = \sqrt{ (\sigma_M \sin(\Delta \phi))^2 + (\sigma_m \cos(\Delta \phi))^2 }.\]Here, \(\sigma_M\) (\(\sigma_m\)) is the major (minor) semiaxis of the Gaussian, and \(\Delta \phi\) is the difference between
phi, the position angle of the Gaussian, and the position angle of the evaluation point.Caveat: For the asymmetric Gaussian, the model is normalized to 1 on the plane, i.e. in small angle approximation: \(N = 1/(2 \pi \sigma_M \sigma_m)\). This means that for huge elongated Gaussians on the sky this model is not correctly normalized. However, this approximation is perfectly acceptable for the more common case of models with modest dimensions: indeed, the error introduced by normalizing on the plane rather than on the sphere is below 0.1% for Gaussians with radii smaller than ~ 5 deg.
Parameters: - lon_0, lat_0 :
Angle Center position
- sigma :
Angle Length of the major semiaxis of the Gaussian, in angular units.
- e :
float Eccentricity of the Gaussian (\(0< e< 1\)).
- phi :
Angle Rotation angle \(\phi\): of the major semiaxis. Increases counter-clockwise from the North direction.
- frame : {“icrs”, “galactic”}
Center position coordinate frame
Examples
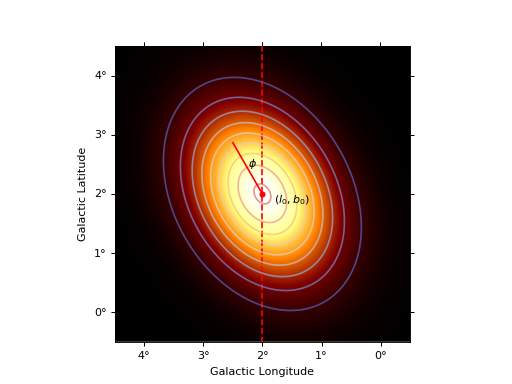
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from astropy.coordinates import Angle from gammapy.modeling.models import GaussianSpatialModel from gammapy.maps import Map, WcsGeom m_geom = WcsGeom.create( binsz=0.01, width=(5, 5), skydir=(2, 2), coordsys="GAL", proj="AIT" ) phi = Angle("30 deg") model = GaussianSpatialModel("2 deg", "2 deg", "1 deg", 0.7, phi, frame="galactic") coords = m_geom.get_coord() vals = model(coords.lon, coords.lat) skymap = Map.from_geom(m_geom, data=vals.value) _, ax, _ = skymap.smooth("0.05 deg").plot() transform = ax.get_transform("galactic") ax.scatter(2, 2, transform=transform, s=20, edgecolor="red", facecolor="red") ax.text(1.5, 1.85, r"$(l_0, b_0)$", transform=transform, ha="center") ax.plot([2, 2 + np.sin(phi)], [2, 2 + np.cos(phi)], color="r", transform=transform) ax.vlines(x=2, color="r", linestyle="--", transform=transform, ymin=-5, ymax=5) ax.text(2.25, 2.45, r"$\phi$", transform=transform) ax.contour(skymap.data, cmap="coolwarm", levels=10, alpha=0.6) plt.show()
Attributes Summary
eevaluation_radiusEvaluation radius ( Angle).framelat_0lon_0parametersParameters ( Parameters)phipositionSpatial model center position sigmatagMethods Summary
__call__(self, lon, lat)Call evaluate method copy(self)A deep copy. create(tag, \*args, \*\*kwargs)Create a model instance. evaluate(lon, lat, lon_0, lat_0, sigma, e, phi)Evaluate model. evaluate_geom(self, geom)Evaluate model on Geom.from_dict(data)to_dict(self)Attributes Documentation
-
e¶
-
frame¶
-
lat_0¶
-
lon_0¶
-
parameters¶ Parameters (
Parameters)
-
phi¶
-
position¶ Spatial model center position
-
sigma¶
-
tag= 'GaussianSpatialModel'¶
Methods Documentation
-
__call__(self, lon, lat)¶ Call evaluate method
-
copy(self)¶ A deep copy.
-
static
create(tag, *args, **kwargs)¶ Create a model instance.
Examples
>>> from gammapy.modeling import Model >>> spectral_model = Model.create("PowerLaw2SpectralModel", amplitude="1e-10 cm-2 s-1", index=3) >>> type(spectral_model) gammapy.modeling.models.spectral.PowerLaw2SpectralModel
-
classmethod
from_dict(data)¶
-
to_dict(self)¶
- lon_0, lat_0 :