DiskSpatialModel¶
-
class
gammapy.modeling.models.DiskSpatialModel(lon_0, lat_0, r_0, e=0, phi='0 deg', edge='0.01 deg', frame='icrs')[source]¶ Bases:
gammapy.modeling.models.SpatialModelConstant disk model.
By default, the model is symmetric, i.e. a disk:
\[\begin{split}\phi(lon, lat) = \frac{1}{2 \pi (1 - \cos{r_0}) } \cdot \begin{cases} 1 & \text{for } \theta \leq r_0 \\ 0 & \text{for } \theta > r_0 \end{cases}\end{split}\]where \(\theta\) is the sky separation. To improve fit convergence of the model, the sharp edges is smoothed using
erf.In case an eccentricity (
e) and rotation angle (\(\phi\)) are passed, then the model is an elongated disk (i.e. an ellipse), with a major semiaxis of length \(r_0\) and position angle \(\phi\) (increaing counter-clockwise from the North direction).The model is defined on the celestial sphere, with a normalization defined by:
\[\int_{4\pi}\phi(\text{lon}, \text{lat}) \,d\Omega = 1\,.\]Parameters: - lon_0, lat_0 :
Angle Center position
- r_0 :
Angle \(a\): length of the major semiaxis, in angular units.
- e :
float Eccentricity of the ellipse (\(0< e< 1\)).
- phi :
Angle Rotation angle \(\phi\): of the major semiaxis. Increases counter-clockwise from the North direction.
- edge :
Angle Width of the edge. The width is defined as the range within the smooth edges of the model drops from 95% to 5% of its amplitude.
- frame : {“icrs”, “galactic”}
Center position coordinate frame
Examples
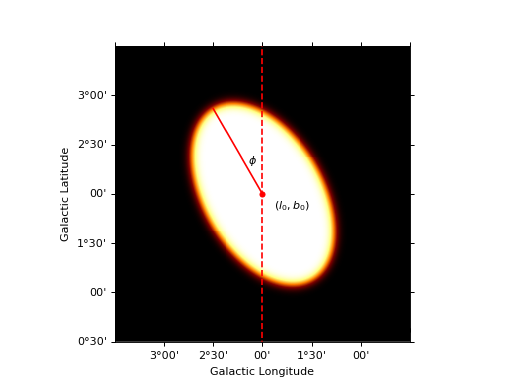
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from gammapy.maps import Map, WcsGeom from gammapy.modeling.models import DiskSpatialModel model = DiskSpatialModel("2 deg", "2 deg", "1 deg", 0.8, "30 deg", frame="galactic") m_geom = WcsGeom.create( binsz=0.01, width=(3, 3), skydir=(2, 2), coordsys="GAL", proj="AIT" ) coords = m_geom.get_coord() vals = model(coords.lon, coords.lat) skymap = Map.from_geom(m_geom, data=vals.value) _, ax, _ = skymap.smooth("0.05 deg").plot() transform = ax.get_transform("galactic") ax.scatter(2, 2, transform=transform, s=20, edgecolor="red", facecolor="red") ax.text(1.7, 1.85, r"$(l_0, b_0)$", transform=transform, ha="center") ax.plot( [2, 2 + np.sin(np.pi / 6)], [2, 2 + np.cos(np.pi / 6)], color="r", transform=transform, ) ax.vlines(x=2, color="r", linestyle="--", transform=transform, ymin=0, ymax=5) ax.text(2.15, 2.3, r"$\phi$", transform=transform) plt.show()
Attributes Summary
eevaluation_radiusEvaluation radius ( Angle).framelat_0lon_0parametersParameters ( Parameters)phipositionSpatial model center position r_0tagMethods Summary
__call__(self, lon, lat)Call evaluate method copy(self)A deep copy. create(tag, \*args, \*\*kwargs)Create a model instance. evaluate(lon, lat, lon_0, lat_0, r_0, e, …)Evaluate model. evaluate_geom(self, geom)Evaluate model on Geom.from_dict(data)to_dict(self)Attributes Documentation
-
e¶
-
frame¶
-
lat_0¶
-
lon_0¶
-
parameters¶ Parameters (
Parameters)
-
phi¶
-
position¶ Spatial model center position
-
r_0¶
-
tag= 'DiskSpatialModel'¶
Methods Documentation
-
__call__(self, lon, lat)¶ Call evaluate method
-
copy(self)¶ A deep copy.
-
static
create(tag, *args, **kwargs)¶ Create a model instance.
Examples
>>> from gammapy.modeling import Model >>> spectral_model = Model.create("PowerLaw2SpectralModel", amplitude="1e-10 cm-2 s-1", index=3) >>> type(spectral_model) gammapy.modeling.models.spectral.PowerLaw2SpectralModel
-
classmethod
from_dict(data)¶
-
to_dict(self)¶
- lon_0, lat_0 :