NaimaModel¶
-
class
gammapy.spectrum.models.NaimaModel(radiative_model, distance=<Quantity 1. kpc>, seed=None)[source]¶ Bases:
gammapy.spectrum.models.SpectralModelA wrapper for Naima models
This class provides an interface with the models defined in the
modelsmodule. The model accepts as a positional argument a Naima radiative model instance, used to compute the non-thermal emission from populations of relativistic electrons or protons due to interactions with the ISM or with radiation and magnetic fields.One of the advantages provided by this class consists in the possibility of performing a maximum likelihood spectral fit of the model’s parameters directly on observations, as opposed to the MCMC fit to flux points featured in Naima. All the parameters defining the parent population of charged particles are stored as
Parameterand left free by default. In case that the radiative model is ` ~naima.radiative.Synchrotron`, the magnetic field strength may also be fitted. Parameters can be freezed/unfreezed before the fit, and maximum/minimum values can be set to limit the parameters space to the physically interesting region.Parameters: - radiative_model :
BaseRadiative An instance of a radiative model defined in
models- distance :
Quantity, optional Distance to the source. If set to 0, the intrinsic differential luminosity will be returned. Default is 1 kpc
- seed : str or list of str, optional
Seed photon field(s) to be considered for the
radiative_modelflux computation, in case of aInverseComptonmodel. It can be a subset of theseed_photon_fieldslist defining theradiative_model. Default is the whole list of photon fields
Examples
Create and plot a spectral model that convolves an
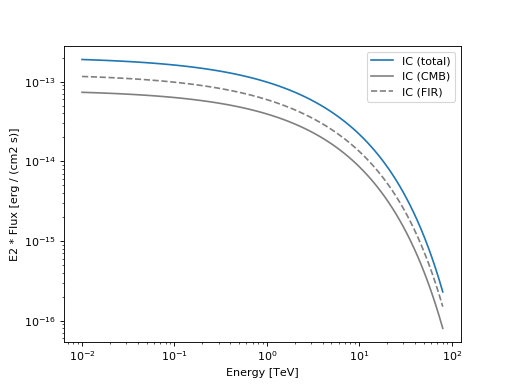
ExponentialCutoffPowerLawelectron distribution with anInverseComptonradiative model, in the presence of multiple seed photon fields.import naima from gammapy.spectrum.models import NaimaModel import astropy.units as u import matplotlib.pyplot as plt particle_distribution = naima.models.ExponentialCutoffPowerLaw(1e30 / u.eV, 10 * u.TeV, 3.0, 30 * u.TeV) radiative_model = naima.radiative.InverseCompton( particle_distribution, seed_photon_fields=[ "CMB", ["FIR", 26.5 * u.K, 0.415 * u.eV / u.cm ** 3], ], Eemin=100 * u.GeV, ) model = NaimaModel(radiative_model, distance=1.5 * u.kpc) opts = { "energy_range" : [10 * u.GeV, 80 * u.TeV], "energy_power" : 2, "flux_unit" : "erg-1 cm-2 s-1", } # Plot the total inverse Compton emission model.plot(label='IC (total)', **opts) # Plot the separate contributions from each seed photon field for seed, ls in zip(['CMB','FIR'], ['-','--']): model = NaimaModel(radiative_model, seed=seed, distance=1.5 * u.kpc) model.plot(label="IC ({})".format(seed), ls=ls, color="gray", **opts) plt.legend(loc='best') plt.show()
Attributes Summary
parametersParameters ( Parameters)Methods Summary
__call__(self, energy)Call evaluate method of derived classes copy(self)A deep copy. energy_flux(self, emin, emax, \*\*kwargs)Compute energy flux in given energy range. energy_flux_error(self, emin, emax, \*\*kwargs)Compute energy flux in given energy range with error propagation. evaluate(self, energy, \*\*kwargs)Evaluate the model evaluate_error(self, energy)Evaluate spectral model with error propagation. from_dict(val)Create from dict. integral(self, emin, emax, \*\*kwargs)Integrate spectral model numerically. integral_error(self, emin, emax, \*\*kwargs)Integrate spectral model numerically with error propagation. inverse(self, value[, emin, emax])Return energy for a given function value of the spectral model. plot(self, energy_range[, ax, energy_unit, …])Plot spectral model curve. plot_error(self, energy_range[, ax, …])Plot spectral model error band. spectral_index(self, energy[, epsilon])Compute spectral index at given energy. to_dict(self)Convert to dict. Attributes Documentation
-
parameters¶ Parameters (
Parameters)
Methods Documentation
-
__call__(self, energy)¶ Call evaluate method of derived classes
-
copy(self)¶ A deep copy.
-
energy_flux(self, emin, emax, **kwargs)¶ Compute energy flux in given energy range.
\[G(E_{min}, E_{max}) = \int_{E_{min}}^{E_{max}} E \phi(E) dE\]Parameters: - emin, emax :
Quantity Lower and upper bound of integration range.
- **kwargs : dict
Keyword arguments passed to func:
integrate_spectrum
- emin, emax :
-
energy_flux_error(self, emin, emax, **kwargs)¶ Compute energy flux in given energy range with error propagation.
\[G(E_{min}, E_{max}) = \int_{E_{min}}^{E_{max}} E \phi(E) dE\]Parameters: - emin, emax :
Quantity Lower bound of integration range.
- **kwargs : dict
Keyword arguments passed to
integrate_spectrum()
Returns: - energy_flux, energy_flux_error : tuple of
Quantity Tuple of energy flux and energy flux error.
- emin, emax :
-
evaluate_error(self, energy)[source]¶ Evaluate spectral model with error propagation.
Parameters: - energy :
Quantity Energy at which to evaluate
Returns: - flux, flux_error : tuple of
Quantity Tuple of flux and flux error.
- energy :
-
classmethod
from_dict(val)¶ Create from dict.
-
integral(self, emin, emax, **kwargs)¶ Integrate spectral model numerically.
\[F(E_{min}, E_{max}) = \int_{E_{min}}^{E_{max}} \phi(E) dE\]If array input for
eminandemaxis given you have to setintervals=Trueif you want the integral in each energy bin.Parameters: - emin, emax :
Quantity Lower and upper bound of integration range.
- **kwargs : dict
Keyword arguments passed to
integrate_spectrum()
- emin, emax :
-
integral_error(self, emin, emax, **kwargs)¶ Integrate spectral model numerically with error propagation.
Parameters: - emin, emax :
Quantity Lower adn upper bound of integration range.
- **kwargs : dict
Keyword arguments passed to func:
integrate_spectrum
Returns: - integral, integral_error : tuple of
Quantity Tuple of integral flux and integral flux error.
- emin, emax :
-
inverse(self, value, emin=<Quantity 0.1 TeV>, emax=<Quantity 100. TeV>)¶ Return energy for a given function value of the spectral model.
Calls the
scipy.optimize.brentqnumerical root finding method.Parameters: Returns: - energy :
Quantity Energies at which the model has the given
value.
- energy :
-
plot(self, energy_range, ax=None, energy_unit='TeV', flux_unit='cm-2 s-1 TeV-1', energy_power=0, n_points=100, **kwargs)¶ Plot spectral model curve.
kwargs are forwarded to
matplotlib.pyplot.plotBy default a log-log scaling of the axes is used, if you want to change the y axis scaling to linear you can use:
from gammapy.spectrum.models import ExponentialCutoffPowerLaw from astropy import units as u pwl = ExponentialCutoffPowerLaw() ax = pwl.plot(energy_range=(0.1, 100) * u.TeV) ax.set_yscale('linear')
Parameters: Returns: - ax :
Axes, optional Axis
- ax :
-
plot_error(self, energy_range, ax=None, energy_unit='TeV', flux_unit='cm-2 s-1 TeV-1', energy_power=0, n_points=100, **kwargs)¶ Plot spectral model error band.
Note
This method calls
ax.set_yscale("log", nonposy='clip')andax.set_xscale("log", nonposx='clip')to create a log-log representation. The additional argumentnonposx='clip'avoids artefacts in the plot, when the error band extends to negative values (see also https://github.com/matplotlib/matplotlib/issues/8623).When you call
plt.loglog()orplt.semilogy()explicitely in your plotting code and the error band extends to negative values, it is not shown correctly. To circumvent this issue also useplt.loglog(nonposx='clip', nonposy='clip')orplt.semilogy(nonposy='clip').Parameters: - ax :
Axes, optional Axis
- energy_range :
Quantity Plot range
- energy_unit : str,
Unit, optional Unit of the energy axis
- flux_unit : str,
Unit, optional Unit of the flux axis
- energy_power : int, optional
Power of energy to multiply flux axis with
- n_points : int, optional
Number of evaluation nodes
- **kwargs : dict
Keyword arguments forwarded to
matplotlib.pyplot.fill_between
Returns: - ax :
Axes, optional Axis
- ax :
-
spectral_index(self, energy, epsilon=1e-05)¶ Compute spectral index at given energy.
Parameters: - energy :
Quantity Energy at which to estimate the index
- epsilon : float
Fractional energy increment to use for determining the spectral index.
Returns: - index : float
Estimated spectral index.
- energy :
-
to_dict(self)¶ Convert to dict.
- radiative_model :