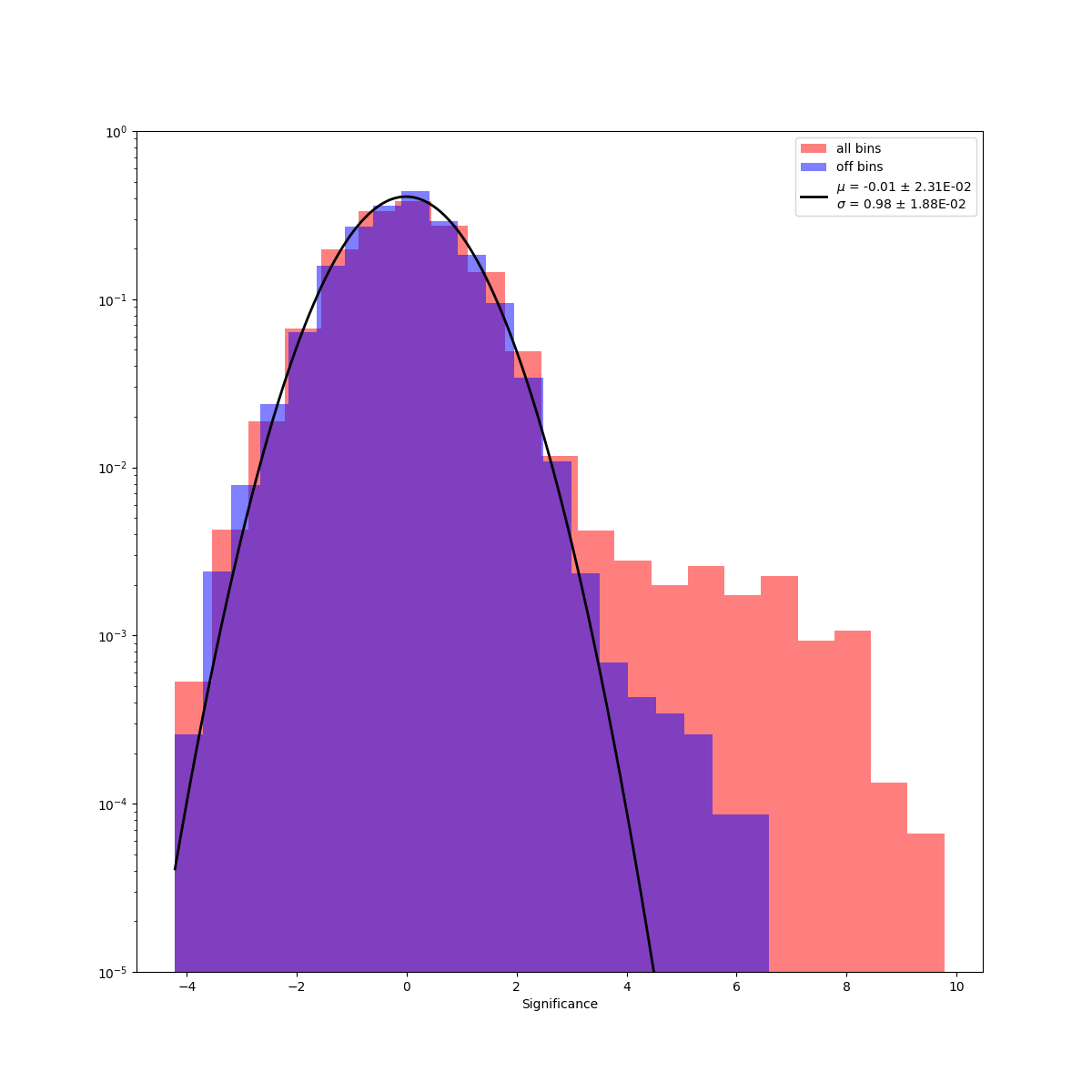
Note
Go to the end to download the full example code or to run this example in your browser via Binder.
Ring background map#
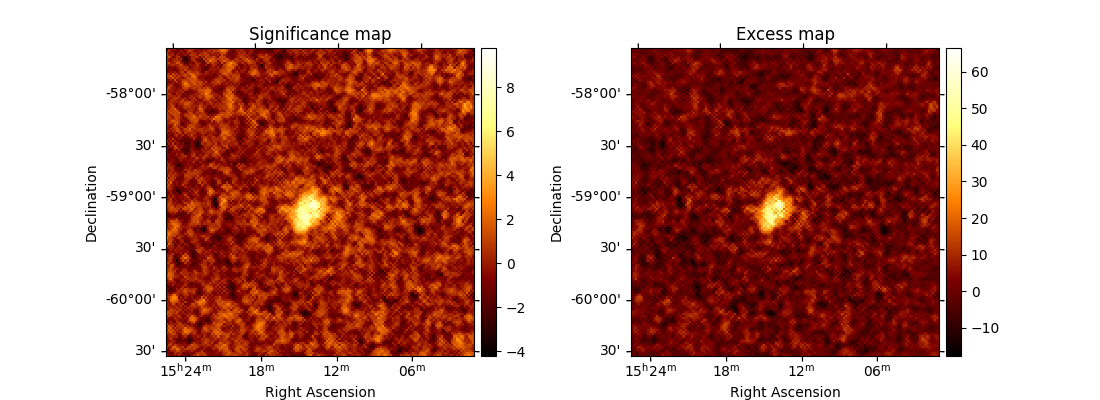
Create an excess (gamma-ray events) and a significance map extracting a ring background.
Context#
One of the challenges of IACT analysis is accounting for the large residual hadronic emission. An excess map, assumed to be a map of only gamma-ray events, requires a good estimate of the background. However, in the absence of a solid template bkg model it is not possible to obtain reliable background model a priori. It was often found necessary in classical cherenkov astronomy to perform a local renormalization of the existing templates, usually with a ring kernel. This assumes that most of the events are background and requires to have an exclusion mask to remove regions with bright signal from the estimation. To read more about this method, see here.
Objective#
Create an excess (gamma-ray events) map of MSH 15-52 as well as a significance map to determine how solid the signal is.
Proposed approach#
The analysis workflow is roughly:
Compute the sky maps keeping each observation separately using the
AnalysisclassEstimate the background using the
RingBackgroundMakerCompute the correlated excess and significance maps using the
ExcessMapEstimator
The normalised background thus obtained can be used for general modelling and fitting.
Setup#
As usual, we’ll start with some general imports…
import logging
# %matplotlib inline
import astropy.units as u
from astropy.coordinates import SkyCoord
from regions import CircleSkyRegion
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from gammapy.analysis import Analysis, AnalysisConfig
from gammapy.datasets import MapDatasetOnOff
from gammapy.estimators import ExcessMapEstimator
from gammapy.makers import RingBackgroundMaker
from gammapy.visualization import plot_distribution
log = logging.getLogger(__name__)
Creating the config file#
Now, we create a config file for out analysis. You may load this from disc if you have a pre-defined config file.
In this example, we will use a few H.E.S.S. runs on the pulsar wind nebula, MSH 1552
# source_pos = SkyCoord.from_name("MSH 15-52")
source_pos = SkyCoord(228.32, -59.08, unit="deg")
config = AnalysisConfig()
# Select observations - 2.5 degrees from the source position
config.observations.datastore = "$GAMMAPY_DATA/hess-dl3-dr1/"
config.observations.obs_cone = {
"frame": "icrs",
"lon": source_pos.ra,
"lat": source_pos.dec,
"radius": 2.5 * u.deg,
}
config.datasets.type = "3d"
config.datasets.geom.wcs.skydir = {
"lon": source_pos.ra,
"lat": source_pos.dec,
"frame": "icrs",
} # The WCS geometry - centered on MSH 15-52
config.datasets.geom.wcs.width = {"width": "3 deg", "height": "3 deg"}
config.datasets.geom.wcs.binsize = "0.02 deg"
# Cutout size (for the run-wise event selection)
config.datasets.geom.selection.offset_max = 2.5 * u.deg
# We now fix the energy axis for the counts map - (the reconstructed energy binning)
config.datasets.geom.axes.energy.min = "0.5 TeV"
config.datasets.geom.axes.energy.max = "10 TeV"
config.datasets.geom.axes.energy.nbins = 10
# We need to extract the ring for each observation separately, hence, no stacking at this stage
config.datasets.stack = False
print(config)
AnalysisConfig
general:
log:
level: info
filename: null
filemode: null
format: null
datefmt: null
outdir: .
n_jobs: 1
datasets_file: null
models_file: null
observations:
datastore: /home/runner/work/gammapy-docs/gammapy-docs/gammapy-datasets/dev/hess-dl3-dr1
obs_ids: []
obs_file: null
obs_cone:
frame: icrs
lon: 228.32 deg
lat: -59.08 deg
radius: 2.5 deg
obs_time:
start: null
stop: null
required_irf:
- aeff
- edisp
- psf
- bkg
datasets:
type: 3d
stack: false
geom:
wcs:
skydir:
frame: icrs
lon: 228.32 deg
lat: -59.08 deg
binsize: 0.02 deg
width:
width: 3.0 deg
height: 3.0 deg
binsize_irf: 0.2 deg
selection:
offset_max: 2.5 deg
axes:
energy:
min: 0.5 TeV
max: 10.0 TeV
nbins: 10
energy_true:
min: 0.5 TeV
max: 20.0 TeV
nbins: 16
map_selection:
- counts
- exposure
- background
- psf
- edisp
background:
method: null
exclusion: null
parameters: {}
safe_mask:
methods:
- aeff-default
parameters: {}
on_region:
frame: null
lon: null
lat: null
radius: null
containment_correction: true
fit:
fit_range:
min: null
max: null
flux_points:
energy:
min: null
max: null
nbins: null
source: source
parameters:
selection_optional: all
excess_map:
correlation_radius: 0.1 deg
parameters: {}
energy_edges:
min: null
max: null
nbins: null
light_curve:
time_intervals:
start: null
stop: null
energy_edges:
min: null
max: null
nbins: null
source: source
parameters:
selection_optional: all
metadata:
creator: Gammapy 2.0.dev3190+g8908f96ba
date: '2026-03-07T05:51:01.670905'
origin: null
Getting the reduced dataset#
We now use the config file to do the initial data reduction which will then be used for a ring extraction
Create the config:
analysis = Analysis(config)
# for this specific case,w e do not need fine bins in true energy
analysis.config.datasets.geom.axes.energy_true = (
analysis.config.datasets.geom.axes.energy
)
# First get the required observations
analysis.get_observations()
print(analysis.config)
# Data extraction:
analysis.get_datasets()
AnalysisConfig
general:
log:
level: INFO
filename: null
filemode: null
format: null
datefmt: null
outdir: .
n_jobs: 1
datasets_file: null
models_file: null
observations:
datastore: /home/runner/work/gammapy-docs/gammapy-docs/gammapy-datasets/dev/hess-dl3-dr1
obs_ids: []
obs_file: null
obs_cone:
frame: icrs
lon: 228.32 deg
lat: -59.08 deg
radius: 2.5 deg
obs_time:
start: null
stop: null
required_irf:
- aeff
- edisp
- psf
- bkg
datasets:
type: 3d
stack: false
geom:
wcs:
skydir:
frame: icrs
lon: 228.32 deg
lat: -59.08 deg
binsize: 0.02 deg
width:
width: 3.0 deg
height: 3.0 deg
binsize_irf: 0.2 deg
selection:
offset_max: 2.5 deg
axes:
energy:
min: 0.5 TeV
max: 10.0 TeV
nbins: 10
energy_true:
min: 0.5 TeV
max: 10.0 TeV
nbins: 10
map_selection:
- counts
- exposure
- background
- psf
- edisp
background:
method: null
exclusion: null
parameters: {}
safe_mask:
methods:
- aeff-default
parameters: {}
on_region:
frame: null
lon: null
lat: null
radius: null
containment_correction: true
fit:
fit_range:
min: null
max: null
flux_points:
energy:
min: null
max: null
nbins: null
source: source
parameters:
selection_optional: all
excess_map:
correlation_radius: 0.1 deg
parameters: {}
energy_edges:
min: null
max: null
nbins: null
light_curve:
time_intervals:
start: null
stop: null
energy_edges:
min: null
max: null
nbins: null
source: source
parameters:
selection_optional: all
metadata:
creator: Gammapy 2.0.dev3190+g8908f96ba
date: '2026-03-07T05:51:01.718656'
origin: null
Extracting the ring background#
Since the ring background is extracted from real off events, we need to
use the Wstat statistics in this case. For this, we will use the
MapDatasetOnOff and the RingBackgroundMaker classes.
Create exclusion mask#
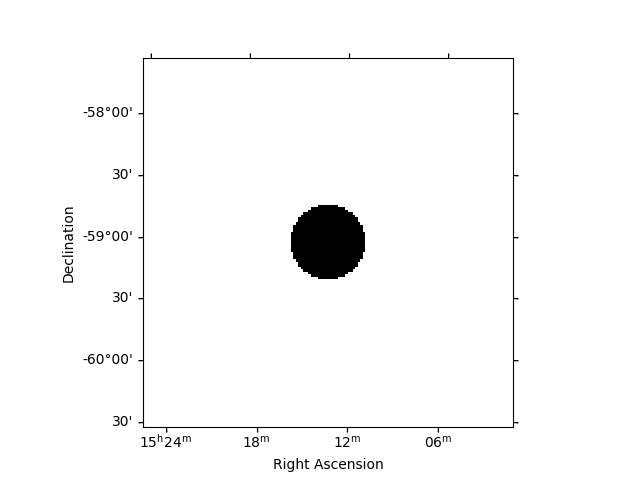
First, we need to create an exclusion mask on the known sources. In this case, we need to mask only MSH 15-52 but this depends on the sources present in our field of view.
# get the geom that we use
geom = analysis.datasets[0].counts.geom
energy_axis = analysis.datasets[0].counts.geom.axes["energy"]
geom_image = geom.to_image().to_cube([energy_axis.squash()])
# Make the exclusion mask
regions = CircleSkyRegion(center=source_pos, radius=0.4 * u.deg)
exclusion_mask = ~geom_image.region_mask([regions])
exclusion_mask.sum_over_axes().plot()
plt.show()
For the present analysis, we use a ring with an inner radius of 0.5 deg and width of 0.3 deg.
ring_maker = RingBackgroundMaker(
r_in="0.5 deg", width="0.3 deg", exclusion_mask=exclusion_mask
)
Create a stacked dataset#
Now, we extract the background for each dataset and then stack the maps together to create a single stacked map for further analysis
energy_axis_true = analysis.datasets[0].exposure.geom.axes["energy_true"]
stacked_on_off = MapDatasetOnOff.create(
geom=geom_image, energy_axis_true=energy_axis_true, name="stacked"
)
for dataset in analysis.datasets:
# Ring extracting makes sense only for 2D analysis
dataset_on_off = ring_maker.run(dataset.to_image())
stacked_on_off.stack(dataset_on_off)
This stacked_on_off has on and off counts and acceptance
maps which we will use in all further analysis. The acceptance and
acceptance_off maps are the system acceptance of gamma-ray like
events in the on and off regions respectively.
print(stacked_on_off)
MapDatasetOnOff
---------------
Name : stacked
Total counts : 41803
Total background counts : 40671.90
Total excess counts : 1131.10
Predicted counts : 40672.37
Predicted background counts : 40672.37
Predicted excess counts : nan
Exposure min : 1.15e+09 m2 s
Exposure max : 1.33e+10 m2 s
Number of total bins : 22500
Number of fit bins : 22500
Fit statistic type : wstat
Fit statistic value (-2 log(L)) : 26475.50
Number of models : 0
Number of parameters : 0
Number of free parameters : 0
Total counts_off : 87621192
Acceptance : 44755
Acceptance off : 96374320