Note
Go to the end to download the full example code or to run this example in your browser via Binder.
3D map simulation#
Simulate a 3D observation of a source with the CTA 1DC response and fit it with the assumed source model.
Prerequisites#
Knowledge of 3D extraction and datasets used in gammapy, see for example the High level interface tutorial.
Context#
To simulate a specific observation, it is not always necessary to simulate the full photon list. For many uses cases, simulating directly a reduced binned dataset is enough: the IRFs reduced in the correct geometry are combined with a source model to predict an actual number of counts per bin. The latter is then used to simulate a reduced dataset using Poisson probability distribution.
This can be done to check the feasibility of a measurement (performance / sensitivity study), to test whether fitted parameters really provide a good fit to the data etc.
Here we will see how to perform a 3D simulation of a CTA observation, assuming both the spectral and spatial morphology of an observed source.
Objective: simulate a 3D observation of a source with CTA using the CTA 1DC response and fit it with the assumed source model.
Proposed approach#
Here we can’t use the regular observation objects that are connected to
a DataStore. Instead, we will create a fake
Observation that contain some pointing information and
the CTA 1DC IRFs (that are loaded with load_irf_dict_from_file).
Next, we will create a MapDataset geometry through
the MapDatasetMaker.
Finally, we will define a model consisting of a
PowerLawSpectralModel and a
GaussianSpatialModel. This model will be assigned to
the dataset and fake the count data.
Imports and versions#
import numpy as np
import astropy.units as u
from astropy.coordinates import SkyCoord
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# %matplotlib inline
from IPython.display import display
from gammapy.data import FixedPointingInfo, Observation, observatory_locations
from gammapy.datasets import MapDataset
from gammapy.irf import load_irf_dict_from_file
from gammapy.makers import MapDatasetMaker, SafeMaskMaker
from gammapy.maps import MapAxis, WcsGeom
from gammapy.modeling import Fit
from gammapy.modeling.models import (
FoVBackgroundModel,
GaussianSpatialModel,
Models,
PowerLawSpectralModel,
SkyModel,
)
Simulation#
We will simulate using the CTA-1DC IRFs shipped with gammapy
# Loading IRFs
irfs = load_irf_dict_from_file(
"$GAMMAPY_DATA/cta-1dc/caldb/data/cta/1dc/bcf/South_z20_50h/irf_file.fits"
)
# Define the observation parameters (typically the observation duration and the pointing position):
livetime = 2.0 * u.hr
pointing_position = SkyCoord(0, 0, unit="deg", frame="galactic")
# We want to simulate an observation pointing at a fixed position in the sky.
# For this, we use the `FixedPointingInfo` class
pointing = FixedPointingInfo(
fixed_icrs=pointing_position.icrs,
)
# Define map geometry for binned simulation
energy_reco = MapAxis.from_edges(
np.logspace(-1.0, 1.0, 10), unit="TeV", name="energy", interp="log"
)
geom = WcsGeom.create(
skydir=(0, 0),
binsz=0.02,
width=(6, 6),
frame="galactic",
axes=[energy_reco],
)
# It is usually useful to have a separate binning for the true energy axis
energy_true = MapAxis.from_edges(
np.logspace(-1.5, 1.5, 30), unit="TeV", name="energy_true", interp="log"
)
empty = MapDataset.create(geom, name="dataset-simu", energy_axis_true=energy_true)
# Define sky model to used simulate the data.
# Here we use a Gaussian spatial model and a Power Law spectral model.
spatial_model = GaussianSpatialModel(
lon_0="0.2 deg", lat_0="0.1 deg", sigma="0.3 deg", frame="galactic"
)
spectral_model = PowerLawSpectralModel(
index=3, amplitude="1e-11 cm-2 s-1 TeV-1", reference="1 TeV"
)
model_simu = SkyModel(
spatial_model=spatial_model,
spectral_model=spectral_model,
name="model-simu",
)
bkg_model = FoVBackgroundModel(dataset_name="dataset-simu")
models = Models([model_simu, bkg_model])
print(models)
/home/runner/work/gammapy-docs/gammapy-docs/gammapy/.tox/build_docs/lib/python3.11/site-packages/astropy/units/core.py:2102: UnitsWarning: '1/s/MeV/sr' did not parse as fits unit: Numeric factor not supported by FITS If this is meant to be a custom unit, define it with 'u.def_unit'. To have it recognized inside a file reader or other code, enable it with 'u.add_enabled_units'. For details, see https://docs.astropy.org/en/latest/units/combining_and_defining.html
warnings.warn(msg, UnitsWarning)
Models
Component 0: SkyModel
Name : model-simu
Datasets names : None
Spectral model type : PowerLawSpectralModel
Spatial model type : GaussianSpatialModel
Temporal model type :
Parameters:
index : 3.000 +/- 0.00
amplitude : 1.00e-11 +/- 0.0e+00 1 / (TeV s cm2)
reference (frozen): 1.000 TeV
lon_0 : 0.200 +/- 0.00 deg
lat_0 : 0.100 +/- 0.00 deg
sigma : 0.300 +/- 0.00 deg
e (frozen): 0.000
phi (frozen): 0.000 deg
Component 1: FoVBackgroundModel
Name : dataset-simu-bkg
Datasets names : ['dataset-simu']
Spectral model type : PowerLawNormSpectralModel
Parameters:
tilt (frozen): 0.000
norm : 1.000 +/- 0.00
reference (frozen): 1.000 TeV
Now, comes the main part of dataset simulation. We create an in-memory
observation and an empty dataset. We then predict the number of counts
for the given model, and Poisson fluctuate it using fake() to make
a simulated counts maps. Keep in mind that it is important to specify
the selection of the maps that you want to produce
# Create an in-memory observation
location = observatory_locations["ctao_south"]
obs = Observation.create(
pointing=pointing, livetime=livetime, irfs=irfs, location=location
)
print(obs)
# Make the MapDataset
maker = MapDatasetMaker(selection=["exposure", "background", "psf", "edisp"])
maker_safe_mask = SafeMaskMaker(methods=["offset-max"], offset_max=4.0 * u.deg)
dataset = maker.run(empty, obs)
dataset = maker_safe_mask.run(dataset, obs)
print(dataset)
# Add the model on the dataset and Poisson fluctuate
dataset.models = models
dataset.fake()
# Do a print on the dataset - there is now a counts maps
print(dataset)
Observation
obs id : 0
tstart : 51544.00
tstop : 51544.08
duration : 7200.00 s
pointing (icrs) : 266.4 deg, -28.9 deg
deadtime fraction : 0.0%
MapDataset
----------
Name : dataset-simu
Total counts : 0
Total background counts : 161250.95
Total excess counts : -161250.95
Predicted counts : 161250.95
Predicted background counts : 161250.95
Predicted excess counts : nan
Exposure min : 4.08e+02 m2 s
Exposure max : 3.58e+10 m2 s
Number of total bins : 810000
Number of fit bins : 804492
Fit statistic type : cash
Fit statistic value (-2 log(L)) : nan
Number of models : 0
Number of parameters : 0
Number of free parameters : 0
MapDataset
----------
Name : dataset-simu
Total counts : 170228
Total background counts : 161250.95
Total excess counts : 8977.05
Predicted counts : 169871.64
Predicted background counts : 161250.95
Predicted excess counts : 8620.69
Exposure min : 4.08e+02 m2 s
Exposure max : 3.58e+10 m2 s
Number of total bins : 810000
Number of fit bins : 804492
Fit statistic type : cash
Fit statistic value (-2 log(L)) : 561030.09
Number of models : 2
Number of parameters : 11
Number of free parameters : 6
Component 0: SkyModel
Name : model-simu
Datasets names : None
Spectral model type : PowerLawSpectralModel
Spatial model type : GaussianSpatialModel
Temporal model type :
Parameters:
index : 3.000 +/- 0.00
amplitude : 1.00e-11 +/- 0.0e+00 1 / (TeV s cm2)
reference (frozen): 1.000 TeV
lon_0 : 0.200 +/- 0.00 deg
lat_0 : 0.100 +/- 0.00 deg
sigma : 0.300 +/- 0.00 deg
e (frozen): 0.000
phi (frozen): 0.000 deg
Component 1: FoVBackgroundModel
Name : dataset-simu-bkg
Datasets names : ['dataset-simu']
Spectral model type : PowerLawNormSpectralModel
Parameters:
tilt (frozen): 0.000
norm : 1.000 +/- 0.00
reference (frozen): 1.000 TeV
Now use this dataset as you would in all standard analysis. You can plot the maps, or proceed with your custom analysis. In the next section, we show the standard 3D fitting as in 3D detailed analysis tutorial.
# To plot, eg, counts:
dataset.counts.smooth(0.05 * u.deg).plot_interactive(add_cbar=True, stretch="linear")
plt.show()
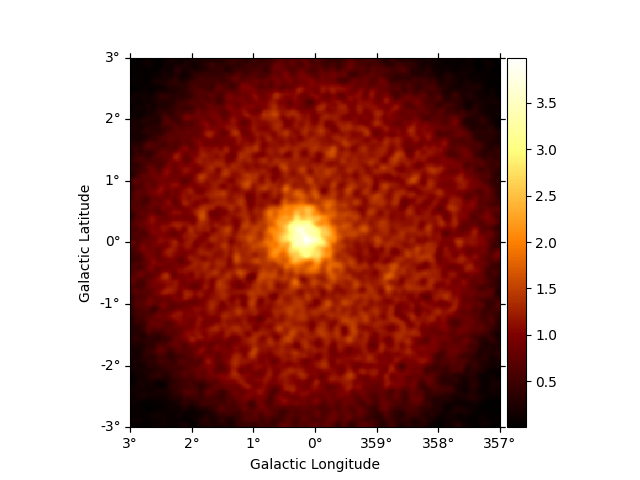
interactive(children=(SelectionSlider(continuous_update=False, description='Select energy:', layout=Layout(width='50%'), options=('100 GeV - 167 GeV', '167 GeV - 278 GeV', '278 GeV - 464 GeV', '464 GeV - 774 GeV', '774 GeV - 1.29 TeV', '1.29 TeV - 2.15 TeV', '2.15 TeV - 3.59 TeV', '3.59 TeV - 5.99 TeV', '5.99 TeV - 10.0 TeV'), style=SliderStyle(description_width='initial'), value='100 GeV - 167 GeV'), RadioButtons(description='Select stretch:', options=('linear', 'sqrt', 'log'), style=DescriptionStyle(description_width='initial'), value='linear'), Output()), _dom_classes=('widget-interact',))
Fit#
In this section, we do a usual 3D fit with the same model used to simulated the data and see the stability of the simulations. Often, it is useful to simulate many such datasets and look at the distribution of the reconstructed parameters.
models_fit = models.copy()
# We do not want to fit the background in this case, so we will freeze the parameters
models_fit["dataset-simu-bkg"].spectral_model.norm.frozen = True
models_fit["dataset-simu-bkg"].spectral_model.tilt.frozen = True
dataset.models = models_fit
print(dataset.models)
fit = Fit(optimize_opts={"print_level": 1})
result = fit.run(datasets=[dataset])
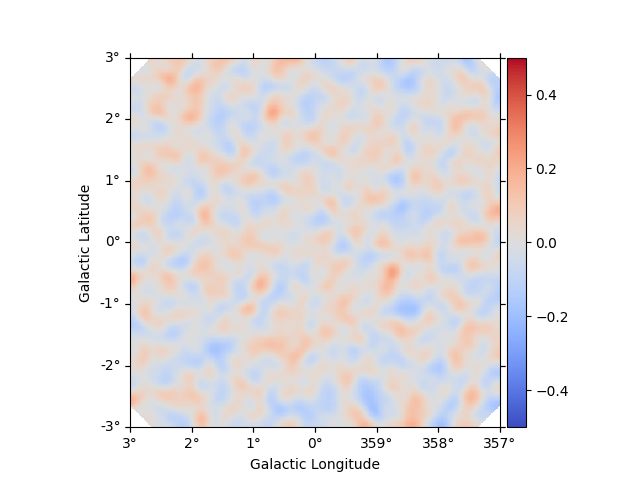
dataset.plot_residuals_spatial(method="diff/sqrt(model)", vmin=-0.5, vmax=0.5)
plt.show()
DatasetModels
Component 0: SkyModel
Name : model-simu
Datasets names : None
Spectral model type : PowerLawSpectralModel
Spatial model type : GaussianSpatialModel
Temporal model type :
Parameters:
index : 3.000 +/- 0.00
amplitude : 1.00e-11 +/- 0.0e+00 1 / (TeV s cm2)
reference (frozen): 1.000 TeV
lon_0 : 0.200 +/- 0.00 deg
lat_0 : 0.100 +/- 0.00 deg
sigma : 0.300 +/- 0.00 deg
e (frozen): 0.000
phi (frozen): 0.000 deg
Component 1: FoVBackgroundModel
Name : dataset-simu-bkg
Datasets names : ['dataset-simu']
Spectral model type : PowerLawNormSpectralModel
Parameters:
tilt (frozen): 0.000
norm (frozen): 1.000
reference (frozen): 1.000 TeV
Compare the injected and fitted models:
print(
"True model: \n",
model_simu,
"\n\n Fitted model: \n",
models_fit["model-simu"],
)
True model:
SkyModel
Name : model-simu
Datasets names : None
Spectral model type : PowerLawSpectralModel
Spatial model type : GaussianSpatialModel
Temporal model type :
Parameters:
index : 3.000 +/- 0.00
amplitude : 1.00e-11 +/- 0.0e+00 1 / (TeV s cm2)
reference (frozen): 1.000 TeV
lon_0 : 0.200 +/- 0.00 deg
lat_0 : 0.100 +/- 0.00 deg
sigma : 0.300 +/- 0.00 deg
e (frozen): 0.000
phi (frozen): 0.000 deg
Fitted model:
SkyModel
Name : model-simu
Datasets names : None
Spectral model type : PowerLawSpectralModel
Spatial model type : GaussianSpatialModel
Temporal model type :
Parameters:
index : 2.999 +/- 0.02
amplitude : 9.71e-12 +/- 3.2e-13 1 / (TeV s cm2)
reference (frozen): 1.000 TeV
lon_0 : 0.205 +/- 0.01 deg
lat_0 : 0.089 +/- 0.01 deg
sigma : 0.293 +/- 0.00 deg
e (frozen): 0.000
phi (frozen): 0.000 deg
Get the errors on the fitted parameters from the parameter table
display(result.parameters.to_table())
type name value unit ... max frozen link prior
---- --------- ---------- -------------- ... --------- ------ ---- -----
index 2.9991e+00 ... nan False
amplitude 9.7084e-12 TeV-1 s-1 cm-2 ... nan False
reference 1.0000e+00 TeV ... nan True
lon_0 2.0485e-01 deg ... nan False
lat_0 8.8765e-02 deg ... 9.000e+01 False
sigma 2.9258e-01 deg ... nan False
e 0.0000e+00 ... 1.000e+00 True
phi 0.0000e+00 deg ... 1.800e+02 True
tilt 0.0000e+00 ... nan True
norm 1.0000e+00 ... nan True
reference 1.0000e+00 TeV ... nan True
