Note
Go to the end to download the full example code. or to run this example in your browser via Binder
Maps#
A thorough tutorial to work with WCS maps.
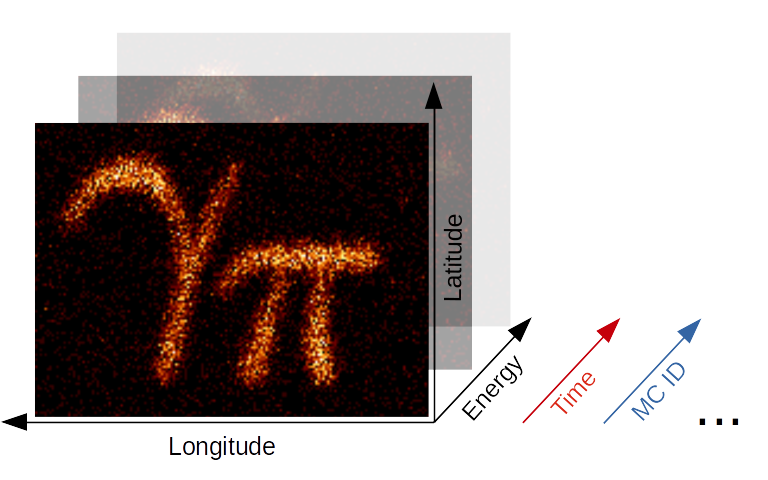
Gammapy Maps Illustration#
Introduction#
The maps submodule contains classes for representing
pixilised data on the sky with an arbitrary number of non-spatial
dimensions such as energy, time, event class or any possible
user-defined dimension (illustrated in the image above). The main
Map data structure features a uniform API for
WCS as well as
HEALPix based images. The
API also generalizes simple image based operations such as smoothing,
interpolation and reprojection to the arbitrary extra dimensions and
makes working with (2 + N)-dimensional hypercubes as easy as working
with a simple 2D image. Further information is also provided on the
maps docs page.
In the following introduction we will learn all the basics of working
with WCS based maps. HEALPix based maps will be covered in a future
tutorial. Make sure you have worked through the Gammapy
overview, because a solid knowledge
about working with SkyCoord and Quantity objects as well as
Numpy is required for this tutorial.
This notebook is rather lengthy, but getting to know the Map data
structure in detail is essential for working with Gammapy and will allow
you to fulfill complex analysis tasks with very few and simple code in
future!
Setup#
import os
# %matplotlib inline
import numpy as np
from astropy import units as u
from astropy.convolution import convolve
from astropy.coordinates import SkyCoord
from astropy.io import fits
from astropy.table import Table
from astropy.time import Time
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from IPython.display import display
from gammapy.data import EventList
from gammapy.maps import (
LabelMapAxis,
Map,
MapAxes,
MapAxis,
TimeMapAxis,
WcsGeom,
WcsNDMap,
)
Check setup#
from gammapy.utils.check import check_tutorials_setup
check_tutorials_setup()
System:
python_executable : /home/runner/work/gammapy-docs/gammapy-docs/gammapy/.tox/build_docs/bin/python
python_version : 3.9.22
machine : x86_64
system : Linux
Gammapy package:
version : 2.0.dev1224+g83b25692c
path : /home/runner/work/gammapy-docs/gammapy-docs/gammapy/.tox/build_docs/lib/python3.9/site-packages/gammapy
Other packages:
numpy : 1.26.4
scipy : 1.13.1
astropy : 6.0.1
regions : 0.8
click : 8.1.8
yaml : 6.0.2
IPython : 8.18.1
jupyterlab : not installed
matplotlib : 3.9.4
pandas : not installed
healpy : 1.17.3
iminuit : 2.31.1
sherpa : 4.16.1
naima : 0.10.0
emcee : 3.1.6
corner : 2.2.3
ray : 2.46.0
Gammapy environment variables:
GAMMAPY_DATA : /home/runner/work/gammapy-docs/gammapy-docs/gammapy-datasets/dev
Creating WCS Maps#
Using Factory Methods#
Maps are most easily created using the create
factory method:
m_allsky = Map.create()
Calling create without any further arguments creates by
default an allsky WCS map using a CAR projection, ICRS coordinates and a
pixel size of 1 deg. This can be easily checked by printing the
geom attribute of the map:
print(m_allsky.geom)
WcsGeom
axes : ['lon', 'lat']
shape : (3600, 1800)
ndim : 2
frame : icrs
projection : CAR
center : 0.0 deg, 0.0 deg
width : 360.0 deg x 180.0 deg
wcs ref : 0.0 deg, 0.0 deg
The geom attribute is a Geom object, that defines the basic
geometry of the map, such as size of the pixels, width and height of the
image, coordinate system etc., but we will learn more about this object
later.
Besides the .geom attribute the map has also a .data attribute,
which is just a plain ~numpy.ndarray and stores the data associated
with this map:
print(m_allsky.data)
[[0. 0. 0. ... 0. 0. 0.]
[0. 0. 0. ... 0. 0. 0.]
[0. 0. 0. ... 0. 0. 0.]
...
[0. 0. 0. ... 0. 0. 0.]
[0. 0. 0. ... 0. 0. 0.]
[0. 0. 0. ... 0. 0. 0.]]
By default maps are filled with zeros.
The map_type argument can be used to control the pixelization scheme
(WCS or HPX).
position = SkyCoord(0.0, 5.0, frame="galactic", unit="deg")
# Create a WCS Map
m_wcs = Map.create(binsz=0.1, map_type="wcs", skydir=position, width=10.0)
# Create a HPX Map
m_hpx = Map.create(binsz=0.1, map_type="hpx", skydir=position, width=10.0)
Here is an example that creates a WCS map centered on the Galactic center and now uses Galactic coordinates:
WcsGeom
axes : ['lon', 'lat']
shape : (500, 250)
ndim : 2
frame : galactic
projection : TAN
center : 0.0 deg, 0.0 deg
width : 10.0 deg x 5.0 deg
wcs ref : 0.0 deg, 0.0 deg
In addition we have defined a TAN projection, a pixel size of 0.02
deg and a width of the map of 10 deg x 5 deg. The width argument
also takes scalar value instead of a tuple, which is interpreted as both
the width and height of the map, so that a quadratic map is created.
Creating from a Map Geometry#
As we have seen in the first examples, the Map object couples the
data (stored as a ndarray) with a Geom object. The
~Geom object can be seen as a generalization of an
astropy.wcs.WCS object, providing the information on how the data
maps to physical coordinate systems. In some cases e.g. when creating
many maps with the same WCS geometry it can be advantageous to first
create the map geometry independent of the map object it-self:
wcs_geom = WcsGeom.create(binsz=0.02, width=(10, 5), skydir=(0, 0), frame="galactic")
And then create the map objects from the wcs_geom geometry
specification:
The Geom object also has a few helpful methods. E.g. we can check
whether a given position on the sky is contained in the map geometry:
# define the position of the Galactic center and anti-center
positions = SkyCoord([0, 180], [0, 0], frame="galactic", unit="deg")
wcs_geom.contains(positions)
array([ True, False])
Or get the image center of the map:
print(wcs_geom.center_skydir)
<SkyCoord (Galactic): (l, b) in deg
(0., 0.)>
Or we can also retrieve the solid angle per pixel of the map:
print(wcs_geom.solid_angle())
[[1.21731921e-07 1.21731921e-07 1.21731921e-07 ... 1.21731921e-07
1.21731921e-07 1.21731921e-07]
[1.21733761e-07 1.21733761e-07 1.21733761e-07 ... 1.21733761e-07
1.21733761e-07 1.21733761e-07]
[1.21735587e-07 1.21735587e-07 1.21735587e-07 ... 1.21735587e-07
1.21735587e-07 1.21735587e-07]
...
[1.21735587e-07 1.21735587e-07 1.21735587e-07 ... 1.21735587e-07
1.21735587e-07 1.21735587e-07]
[1.21733761e-07 1.21733761e-07 1.21733761e-07 ... 1.21733761e-07
1.21733761e-07 1.21733761e-07]
[1.21731921e-07 1.21731921e-07 1.21731921e-07 ... 1.21731921e-07
1.21731921e-07 1.21731921e-07]] sr
Adding Non-Spatial Axes#
In many analysis scenarios we would like to add extra dimension to the
maps to study e.g. energy or time dependency of the data. Those
non-spatial dimensions are handled with the MapAxis object. Let us
first define an energy axis, with 4 bins:
energy_axis = MapAxis.from_bounds(
1, 100, nbin=4, unit="TeV", name="energy", interp="log"
)
print(energy_axis)
MapAxis
name : energy
unit : 'TeV'
nbins : 4
node type : edges
edges min : 1.0e+00 TeV
edges max : 1.0e+02 TeV
interp : log
Where interp='log' specifies that a logarithmic spacing is used
between the bins, equivalent to np.logspace(0, 2, 4). This
MapAxis object we can now pass to create() using the
axes= argument:
m_cube = Map.create(binsz=0.02, width=(10, 5), frame="galactic", axes=[energy_axis])
print(m_cube.geom)
WcsGeom
axes : ['lon', 'lat', 'energy']
shape : (500, 250, 4)
ndim : 3
frame : galactic
projection : CAR
center : 0.0 deg, 0.0 deg
width : 10.0 deg x 5.0 deg
wcs ref : 0.0 deg, 0.0 deg
Now we see that besides lon and lat the map has an additional
axes named energy with 4 bins. The total dimension of the map is now
ndim=3.
We can also add further axes by passing a list of MapAxis objects.
To demonstrate this we create a time axis with linearly spaced bins and
pass both axes to Map.create():
time_axis = MapAxis.from_bounds(0, 24, nbin=24, unit="hour", name="time", interp="lin")
m_4d = Map.create(
binsz=0.02, width=(10, 5), frame="galactic", axes=[energy_axis, time_axis]
)
print(m_4d.geom)
WcsGeom
axes : ['lon', 'lat', 'energy', 'time']
shape : (500, 250, 4, 24)
ndim : 4
frame : galactic
projection : CAR
center : 0.0 deg, 0.0 deg
width : 10.0 deg x 5.0 deg
wcs ref : 0.0 deg, 0.0 deg
The MapAxis object internally stores the coordinates or “position
values” associated with every map axis bin or “node”. We distinguish
between two node types: "edges" and "center". The node type
"edges"(which is also the default) specifies that the data
associated with this axis is integrated between the edges of the bin
(e.g. counts data). The node type "center" specifies that the data is
given at the center of the bin (e.g. exposure or differential fluxes).
The edges of the bins can be checked with edges attribute:
print(energy_axis.edges)
[ 1. 3.16227766 10. 31.6227766 100. ] TeV
The numbers are given in the units we specified above, which can be checked again with:
print(energy_axis.unit)
TeV
The centers of the axis bins can be checked with the center
attribute:
print(energy_axis.center)
[ 1.77827941 5.62341325 17.7827941 56.23413252] TeV
Adding Non-contiguous axes#
Non-spatial map axes can also be handled through two other objects known as the TimeMapAxis
and the LabelMapAxis.
TimeMapAxis#
The TimeMapAxis object provides an axis for non-adjacent
time intervals.
time_map_axis = TimeMapAxis(
edges_min=[1, 5, 10, 15] * u.day,
edges_max=[2, 7, 13, 18] * u.day,
reference_time=Time("2020-03-19"),
)
print(time_map_axis)
TimeMapAxis
-----------
name : time
nbins : 4
reference time : 2020-03-19 00:00:00.000
scale : utc
time min. : 2020-03-20 00:00:00.000
time max. : 2020-04-06 00:00:00.000
total time : 216.0 h
This time_map_axis can then be utilised in a similar way to the previous implementation to create
a Map.
map_4d = Map.create(
binsz=0.02, width=(10, 5), frame="galactic", axes=[energy_axis, time_map_axis]
)
print(map_4d.geom)
WcsGeom
axes : ['lon', 'lat', 'energy', 'time']
shape : (500, 250, 4, 4)
ndim : 4
frame : galactic
projection : CAR
center : 0.0 deg, 0.0 deg
width : 10.0 deg x 5.0 deg
wcs ref : 0.0 deg, 0.0 deg
It is possible to utilise the slice attrribute
to create new a TimeMapAxis. Here we are slicing
between the first and third axis to extract the subsection of the axis
between indice 0 and 2.
print(time_map_axis.slice([0, 2]))
TimeMapAxis
-----------
name : time
nbins : 2
reference time : 2020-03-19 00:00:00.000
scale : utc
time min. : 2020-03-20 00:00:00.000
time max. : 2020-04-01 00:00:00.000
total time : 96.0 h
It is also possible to squash the axis,
which squashes the existing axis into one bin. This creates a new axis
between the extreme edges of the initial axis.
print(time_map_axis.squash())
TimeMapAxis
-----------
name : time
nbins : 1
reference time : 2020-03-19 00:00:00.000
scale : utc
time min. : 2020-03-20 00:00:00.000
time max. : 2020-04-06 00:00:00.000
total time : 408.0 h
The is_contiguous method returns a boolean
which indicates whether the TimeMapAxis is contiguous or not.
print(time_map_axis.is_contiguous)
False
As we have a non-contiguous axis we can print the array of bin edges for both
the minimum axis edges (edges_min) and the maximum axis
edges (edges_max).
print(time_map_axis.edges_min)
print(time_map_axis.edges_max)
[ 1. 5. 10. 15.] d
[ 2. 7. 13. 18.] d
Next, we use the to_contiguous functionality to
create a contiguous axis and expose edges. This
method returns a Quantity with respect to the reference time.
True
[ 1. 2. 5. 7. 10. 13. 15. 18.] d
The time_edges will return the Time object directly
['2020-03-20 00:00:00.000' '2020-03-21 00:00:00.000'
'2020-03-24 00:00:00.000' '2020-03-26 00:00:00.000'
'2020-03-29 00:00:00.000' '2020-04-01 00:00:00.000'
'2020-04-03 00:00:00.000' '2020-04-06 00:00:00.000']
TimeMapAxis also has both functionalities of
coord_to_pix and coord_to_idx.
The coord_to_idx attribute will give the index of the
time specified, similarly for coord_to_pix which returns
the pixel. A linear interpolation is assumed.
Start by choosing a time which we know is within the TimeMapAxis and see the results.
time = Time(time_map_axis.time_max.mjd[0], format="mjd")
print(time_map_axis.coord_to_pix(time))
print(time_map_axis.coord_to_idx(time))
[0.5]
0
This functionality can also be used with an array of Time values.
times = Time(time_map_axis.time_max.mjd, format="mjd")
print(time_map_axis.coord_to_pix(times))
print(time_map_axis.coord_to_idx(times))
[0.5 1.5 2.5 3.5]
[0 1 2 3]
Note here we take a Time which is outside the edges.
A linear interpolation is assumed for both methods, therefore for a time
outside the time_map_axis there is no extrapolation and -1 is returned.
Note: due to this, the coord_to_pix method will
return nan and the coord_to_idx method returns -1.
print(time_map_axis.coord_to_pix(Time(time.mjd + 1, format="mjd")))
print(time_map_axis.coord_to_idx(Time(time.mjd + 1, format="mjd")))
[nan]
-1
LabelMapAxis#
The LabelMapAxis object allows for handling of labels for map axes.
It provides an axis for non-numeric entries.
label_axis = LabelMapAxis(
labels=["dataset-1", "dataset-2", "dataset-3"], name="dataset"
)
print(label_axis)
LabelMapAxis
------------
name : dataset
nbins : 3
node type : label
labels : ['dataset-1', 'dataset-2', 'dataset-3']
The labels can be checked using the center attribute:
print(label_axis.center)
['dataset-1' 'dataset-2' 'dataset-3']
To obtain the position of the label, one can utilise the coord_to_pix attribute
print(label_axis.coord_to_pix(["dataset-3"]))
[2.]
To adapt and create new axes the following attributes can be utilised:
concatenate, slice and
squash.
Combining two different LabelMapAxis is done in the following way:
label_axis2 = LabelMapAxis(labels=["dataset-a", "dataset-b"], name="dataset")
print(label_axis.concatenate(label_axis2))
LabelMapAxis
------------
name : dataset
nbins : 5
node type : label
labels : ['dataset-1', 'dataset-2', 'dataset-3', 'dataset-a', 'dataset-b']
A new LabelMapAxis can be created by slicing an already existing one.
Here we are slicing between the second and third bins to extract the subsection.
print(label_axis.slice([1, 2]))
LabelMapAxis
------------
name : dataset
nbins : 2
node type : label
labels : ['dataset-2', 'dataset-3']
A new axis object can be created by squashing the axis into a single bin.
print(label_axis.squash())
LabelMapAxis
------------
name : dataset
nbins : 1
node type : label
labels : ['dataset-1...dataset-3']
Mixing the three previous axis types (MapAxis,
TimeMapAxis and LabelMapAxis)
would be done like so:
axes = MapAxes(axes=[energy_axis, time_map_axis, label_axis])
hdu = axes.to_table_hdu(format="gadf")
table = Table.read(hdu)
display(table)
CHANNEL ENERGY E_MIN ... TIME_MIN TIME_MAX DATASET
TeV TeV ... d d
------- ------------------ ------------------ ... -------- -------- ---------
0 1.778279410038923 1.0 ... 1.0 2.0 dataset-1
1 1.778279410038923 1.0 ... 1.0 2.0 dataset-2
2 1.778279410038923 1.0 ... 1.0 2.0 dataset-3
3 5.623413251903492 3.1622776601683795 ... 1.0 2.0 dataset-1
4 5.623413251903492 3.1622776601683795 ... 1.0 2.0 dataset-2
5 5.623413251903492 3.1622776601683795 ... 1.0 2.0 dataset-3
6 17.78279410038923 10.000000000000002 ... 1.0 2.0 dataset-1
7 17.78279410038923 10.000000000000002 ... 1.0 2.0 dataset-2
8 17.78279410038923 10.000000000000002 ... 1.0 2.0 dataset-3
9 56.234132519034915 31.62277660168379 ... 1.0 2.0 dataset-1
... ... ... ... ... ... ...
38 1.778279410038923 1.0 ... 15.0 18.0 dataset-3
39 5.623413251903492 3.1622776601683795 ... 15.0 18.0 dataset-1
40 5.623413251903492 3.1622776601683795 ... 15.0 18.0 dataset-2
41 5.623413251903492 3.1622776601683795 ... 15.0 18.0 dataset-3
42 17.78279410038923 10.000000000000002 ... 15.0 18.0 dataset-1
43 17.78279410038923 10.000000000000002 ... 15.0 18.0 dataset-2
44 17.78279410038923 10.000000000000002 ... 15.0 18.0 dataset-3
45 56.234132519034915 31.62277660168379 ... 15.0 18.0 dataset-1
46 56.234132519034915 31.62277660168379 ... 15.0 18.0 dataset-2
47 56.234132519034915 31.62277660168379 ... 15.0 18.0 dataset-3
Length = 48 rows
Reading and Writing#
Gammapy Map objects are serialized using the Flexible Image
Transport Format (FITS). Depending on the pixelization scheme (HEALPix
or WCS) and presence of non-spatial dimensions the actual convention to
write the FITS file is different. By default Gammapy uses a generic
convention named "gadf", which will support WCS and HEALPix formats as
well as an arbitrary number of non-spatial axes. The convention is
documented in detail on the Gamma Astro Data
Formats
page.
Other conventions required by specific software (e.g. the Fermi Science Tools) are supported as well. At the moment those are the following
"fgst-ccube": Fermi counts cube format."fgst-ltcube": Fermi livetime cube format."fgst-bexpcube": Fermi exposure cube format"fgst-template": Fermi Galactic diffuse and source template format."fgst-srcmap"and"fgst-srcmap-sparse": Fermi source map and sparse source map format.
The conventions listed above only support an additional energy axis.
Reading Maps#
Reading FITS files is mainly exposed via the read() method. Let
us take a look at a first example:
WcsNDMap
geom : WcsGeom
axes : ['lon', 'lat']
shape : (400, 200)
ndim : 2
unit :
dtype : >i8
If map_type argument is not given when calling read a map object
will be instantiated with the pixelization of the input HDU.
By default Map.read() will try to find the first valid data hdu in
the filename and read the data from there. If multiple HDUs are present
in the FITS file, the desired one can be chosen with the additional
hdu= argument:
WcsNDMap
geom : WcsGeom
axes : ['lon', 'lat']
shape : (400, 200)
ndim : 2
unit :
dtype : >i8
In rare cases e.g. when the FITS file is not valid or meta data is
missing from the header it can be necessary to modify the header of a
certain HDU before creating the Map object. In this case we can use
astropy.io.fits directly to read the FITS file:
filename = os.environ["GAMMAPY_DATA"] + "/fermi-3fhl-gc/fermi-3fhl-gc-exposure.fits.gz"
hdulist = fits.open(filename)
print(hdulist.info())
Filename: /home/runner/work/gammapy-docs/gammapy-docs/gammapy-datasets/dev/fermi-3fhl-gc/fermi-3fhl-gc-exposure.fits.gz
No. Name Ver Type Cards Dimensions Format
0 PRIMARY 1 PrimaryHDU 23 (400, 200) float32
None
And then modify the header keyword and use Map.from_hdulist() to
create the Map object after:
hdulist["PRIMARY"].header["BUNIT"] = "cm2 s"
print(Map.from_hdulist(hdulist=hdulist))
WcsNDMap
geom : WcsGeom
axes : ['lon', 'lat']
shape : (400, 200)
ndim : 2
unit : cm2 s
dtype : >f4
Writing Maps#
Writing FITS files on disk via the Map.write() method.
Here is a first example:
m_cube.write("example_cube.fits", overwrite=True)
By default Gammapy does not overwrite files. In this example we set
overwrite=True in case the cell gets executed multiple times. Now we
can read back the cube from disk using Map.read():
WcsNDMap
geom : WcsGeom
axes : ['lon', 'lat', 'energy']
shape : (500, 250, 4)
ndim : 3
unit :
dtype : >f4
We can also choose a different FITS convention to write the example cube in a format compatible to the Fermi Galactic diffuse background model:
m_cube.write("example_cube_fgst.fits", format="fgst-template", overwrite=True)
To understand a little bit better the generic gadf convention we use
Map.to_hdulist() to generate a list of FITS HDUs first:
hdulist = m_4d.to_hdulist(format="gadf")
print(hdulist.info())
Filename: (No file associated with this HDUList)
No. Name Ver Type Cards Dimensions Format
0 PRIMARY 1 PrimaryHDU 30 (500, 250, 4, 24) float32
1 PRIMARY_BANDS 1 BinTableHDU 33 96R x 7C ['K', 'D', 'D', 'D', 'D', 'D', 'D']
None
As we can see the HDUList object contains to HDUs. The first one
named PRIMARY contains the data array with shape corresponding to
our data and the WCS information stored in the header:
print(hdulist["PRIMARY"].header)
SIMPLE = T / conforms to FITS standard BITPIX = -32 / array data type NAXIS = 4 / number of array dimensions NAXIS1 = 500 NAXIS2 = 250 NAXIS3 = 4 NAXIS4 = 24 EXTEND = T WCSAXES = 2 / Number of coordinate axes CRPIX1 = 250.5 / Pixel coordinate of reference point CRPIX2 = 125.5 / Pixel coordinate of reference point CDELT1 = -0.02 / [deg] Coordinate increment at reference point CDELT2 = 0.02 / [deg] Coordinate increment at reference point CUNIT1 = 'deg' / Units of coordinate increment and value CUNIT2 = 'deg' / Units of coordinate increment and value CTYPE1 = 'GLON-CAR' / Galactic longitude, plate caree projection CTYPE2 = 'GLAT-CAR' / Galactic latitude, plate caree projection CRVAL1 = 0.0 / [deg] Coordinate value at reference point CRVAL2 = 0.0 / [deg] Coordinate value at reference point LONPOLE = 0.0 / [deg] Native longitude of celestial pole LATPOLE = 90.0 / [deg] Native latitude of celestial pole MJDREF = 0.0 / [d] MJD of fiducial time AXCOLS1 = 'E_MIN,E_MAX' INTERP1 = 'log ' AXCOLS2 = 'TIME_MIN,TIME_MAX' INTERP2 = 'lin ' WCSSHAPE= '(500,250,4,24)' BANDSHDU= 'PRIMARY_BANDS' META = '{} ' BUNIT = '' END
The second HDU is a BinTableHDU named PRIMARY_BANDS contains the
information on the non-spatial axes such as name, order, unit, min, max
and center values of the axis bins. We use an astropy.table.Table to
show the information:
print(Table.read(hdulist["PRIMARY_BANDS"]))
CHANNEL ENERGY E_MIN ... TIME TIME_MIN TIME_MAX
TeV TeV ... h h h
------- ------------------ ------------------ ... ---- -------- --------
0 1.778279410038923 1.0 ... 0.5 0.0 1.0
1 5.623413251903492 3.1622776601683795 ... 0.5 0.0 1.0
2 17.78279410038923 10.000000000000002 ... 0.5 0.0 1.0
3 56.234132519034915 31.62277660168379 ... 0.5 0.0 1.0
4 1.778279410038923 1.0 ... 1.5 1.0 2.0
5 5.623413251903492 3.1622776601683795 ... 1.5 1.0 2.0
6 17.78279410038923 10.000000000000002 ... 1.5 1.0 2.0
7 56.234132519034915 31.62277660168379 ... 1.5 1.0 2.0
8 1.778279410038923 1.0 ... 2.5 2.0 3.0
9 5.623413251903492 3.1622776601683795 ... 2.5 2.0 3.0
... ... ... ... ... ... ...
86 17.78279410038923 10.000000000000002 ... 21.5 21.0 22.0
87 56.234132519034915 31.62277660168379 ... 21.5 21.0 22.0
88 1.778279410038923 1.0 ... 22.5 22.0 23.0
89 5.623413251903492 3.1622776601683795 ... 22.5 22.0 23.0
90 17.78279410038923 10.000000000000002 ... 22.5 22.0 23.0
91 56.234132519034915 31.62277660168379 ... 22.5 22.0 23.0
92 1.778279410038923 1.0 ... 23.5 23.0 24.0
93 5.623413251903492 3.1622776601683795 ... 23.5 23.0 24.0
94 17.78279410038923 10.000000000000002 ... 23.5 23.0 24.0
95 56.234132519034915 31.62277660168379 ... 23.5 23.0 24.0
Length = 96 rows
Maps can be serialized to a sparse data format by calling write with
sparse=True. This will write all non-zero pixels in the map to a
data table appropriate to the pixelization scheme.
Accessing Data#
How to get data values#
All map objects have a set of accessor methods, which can be used to
access or update the contents of the map irrespective of its underlying
representation. Those accessor methods accept as their first argument a
coordinate tuple containing scalars, list, or numpy.ndarray
with one tuple element for each dimension. Some methods additionally
accept a dict or MapCoord argument, of which both allow to
assign coordinates by axis name.
Let us first begin with the get_by_idx() method, that accepts a
tuple of indices. The order of the indices corresponds to the axis order
of the map:
print(m_gc.get_by_idx((50, 30)))
[0.]
Important: Gammapy uses a reversed index order in the map API with the longitude axes first. To achieve the same by directly indexing into the numpy array we have to call:
print(m_gc.data[([30], [50])])
[0.]
To check the order of the axes you can always print the .geom`
attribute:
print(m_gc.geom)
WcsGeom
axes : ['lon', 'lat']
shape : (500, 250)
ndim : 2
frame : galactic
projection : TAN
center : 0.0 deg, 0.0 deg
width : 10.0 deg x 5.0 deg
wcs ref : 0.0 deg, 0.0 deg
To access values directly by sky coordinates we can use the
get_by_coord() method. This time we pass in a dict, specifying
the axes names corresponding to the given coordinates:
print(m_gc.get_by_coord({"lon": [0, 180], "lat": [0, 0]}))
[ 0. nan]
The units of the coordinates are assumed to be in degrees in the
coordinate system used by the map. If the coordinates do not correspond
to the exact pixel center, the value of the nearest pixel center will be
returned. For positions outside the map geometry np.nan is returned.
The coordinate or idx arrays follow normal Numpy broadcasting rules. So the following works as expected:
lons = np.linspace(-4, 4, 10)
print(m_gc.get_by_coord({"lon": lons, "lat": 0}))
[0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.]
Or as an even more advanced example, we can provide lats as column
vector and broadcasting to a 2D result array will be applied:
lons = np.linspace(-4, 4, 8)
lats = np.linspace(-4, 4, 8).reshape(-1, 1)
print(m_gc.get_by_coord({"lon": lons, "lat": lats}))
[[nan nan nan nan nan nan nan nan]
[nan nan nan nan nan nan nan nan]
[ 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.]
[ 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.]
[ 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.]
[ 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.]
[nan nan nan nan nan nan nan nan]
[nan nan nan nan nan nan nan nan]]
Indexing and Slicing Sub-Maps#
When you have worked with Numpy arrays in the past you are probably
familiar with the concept of indexing and slicing into data arrays. To
support slicing of non-spatial axes of Map objects, the Map
object has a slice_by_idx() method, which allows to extract
sub-maps from a larger map.
The following example demonstrates how to get the map at the energy bin number 3:
m_sub = m_cube.slice_by_idx({"energy": 3})
print(m_sub)
WcsNDMap
geom : WcsGeom
axes : ['lon', 'lat']
shape : (500, 250)
ndim : 2
unit :
dtype : >f4
Note that the returned object is again a Map with updated axes
information. In this case, because we extracted only a single image, the
energy axes is dropped from the map.
To extract a sub-cube with a sliced energy axes we can use a normal
slice() object:
m_sub = m_cube.slice_by_idx({"energy": slice(1, 3)})
print(m_sub)
WcsNDMap
geom : WcsGeom
axes : ['lon', 'lat', 'energy']
shape : (500, 250, 2)
ndim : 3
unit :
dtype : >f4
Note that the returned object is also a Map object, but this time
with updated energy axis specification.
Slicing of multiple dimensions is supported by adding further entries to
the dict passed to slice_by_idx()
m_sub = m_4d.slice_by_idx({"energy": slice(1, 3), "time": slice(4, 10)})
print(m_sub)
WcsNDMap
geom : WcsGeom
axes : ['lon', 'lat', 'energy', 'time']
shape : (500, 250, 2, 6)
ndim : 4
unit :
dtype : float32
For convenience there is also a get_image_by_coord() method which
allows to access image planes at given non-spatial physical coordinates.
This method also supports Quantity objects:
image = m_4d.get_image_by_coord({"energy": 4 * u.TeV, "time": 5 * u.h})
print(image.geom)
WcsGeom
axes : ['lon', 'lat']
shape : (500, 250)
ndim : 2
frame : galactic
projection : CAR
center : 0.0 deg, 0.0 deg
width : 10.0 deg x 5.0 deg
wcs ref : 0.0 deg, 0.0 deg
Iterating by image#
For maps with non-spatial dimensions the iter_by_image_data
method can be used to loop over image slices. The image plane index
idx is returned in data order, so that the data array can be indexed
directly. Here is an example for an in-place convolution of an image
using convolve to interpolate NaN values:
axis1 = MapAxis([1, 10, 100], interp="log", name="energy")
axis2 = MapAxis([1, 2, 3], interp="lin", name="time")
m = Map.create(width=(5, 3), axes=[axis1, axis2], binsz=0.1)
m.data[:, :, 15:18, 20:25] = np.nan
for img, idx in m.iter_by_image_data():
kernel = np.ones((5, 5))
m.data[idx] = convolve(img, kernel)
assert not np.isnan(m.data).any()
Modifying Data#
How to set data values#
To modify and set map data values the Map object features as well a
set_by_idx() method:
m_cube.set_by_idx(idx=(10, 20, 3), vals=42)
here we check that data have been updated:
print(m_cube.get_by_idx((10, 20, 3)))
[42.]
Of course there is also a set_by_coord() method, which allows to
set map data values in physical coordinates.
m_cube.set_by_coord({"lon": 0, "lat": 0, "energy": 2 * u.TeV}, vals=42)
Again the lon and lat values are assumed to be given in degrees
in the coordinate system used by the map. For the energy axis, the unit
is the one specified on the axis (use m_cube.geom.axes[0].unit to
check if needed…).
All .xxx_by_coord() methods accept SkyCoord objects as well. In
this case we have to use the "skycoord" keyword instead of "lon" and
"lat":
skycoords = SkyCoord([1.2, 3.4], [-0.5, 1.1], frame="galactic", unit="deg")
m_cube.set_by_coord({"skycoord": skycoords, "energy": 2 * u.TeV}, vals=42)
Filling maps from event lists#
This example shows how to fill a counts cube from an event list:
energy_axis = MapAxis.from_bounds(
10.0, 2e3, 12, interp="log", name="energy", unit="GeV"
)
counts_3d = WcsNDMap.create(
binsz=0.1, width=10.0, skydir=(0, 0), frame="galactic", axes=[energy_axis]
)
events = EventList.read("$GAMMAPY_DATA/fermi-3fhl-gc/fermi-3fhl-gc-events.fits.gz")
counts_3d.fill_by_coord({"skycoord": events.radec, "energy": events.energy})
counts_3d.write("ccube.fits", format="fgst-ccube", overwrite=True)
Alternatively you can use the fill_events method:
counts_3d = WcsNDMap.create(
binsz=0.1, width=10.0, skydir=(0, 0), frame="galactic", axes=[energy_axis]
)
counts_3d.fill_events(events)
If you have a given map already, and want to make a counts image with
the same geometry (not using the pixel data from the original map), you
can also use the fill_events method.
events = EventList.read("$GAMMAPY_DATA/fermi-3fhl-gc/fermi-3fhl-gc-events.fits.gz")
reference_map = Map.read("$GAMMAPY_DATA/fermi-3fhl-gc/fermi-3fhl-gc-counts.fits.gz")
counts = Map.from_geom(reference_map.geom)
counts.fill_events(events)
It works for IACT and Fermi-LAT events, for WCS or HEALPix map geometries, and also for extra axes. Especially energy axes are automatically handled correctly.
Filling maps from interpolation#
Maps support interpolation via the interp_by_coord and
interp_by_pix methods. Currently, the following interpolation
methods are supported:
"nearest": Return value of nearest pixel (no interpolation)."linear": Interpolation with first order polynomial. This is the only interpolation method that is supported for all map types.quadratic: Interpolation with second order polynomial.cubic: Interpolation with third order polynomial.
Note that "quadratic" and "cubic" interpolation are currently only
supported for WCS-based maps with regular geometry (e.g. 2D or ND with
the same geometry in every image plane). "linear" and higher order
interpolation by pixel coordinates is only supported for WCS-based maps.
In the following example we create a new map and fill it by interpolating another map:
# read map
filename = "$GAMMAPY_DATA/fermi-3fhl-gc/gll_iem_v06_gc.fits.gz"
m_iem_gc = Map.read(filename)
# create new geometry
skydir = SkyCoord(266.4, -28.9, frame="icrs", unit="deg")
wcs_geom_cel = WcsGeom.create(skydir=skydir, binsz=0.1, frame="icrs", width=(8, 4))
# create new empty map from geometry
m_iem_10GeV = Map.from_geom(wcs_geom_cel)
coords = m_iem_10GeV.geom.get_coord()
# fill new map using interpolation
m_iem_10GeV.data = m_iem_gc.interp_by_coord(
{"skycoord": coords.skycoord, "energy_true": 10 * u.GeV},
method="linear",
fill_value=np.nan,
)
Interpolating onto a different geometry#
For 3d geometries this operation can be performed directly using the
interp_to_geom() method. This is very useful, ex: while using map
arithmetic.
# create new geometry
energy_axis = MapAxis.from_bounds(
10.0, 2e3, 6, interp="log", name="energy_true", unit="GeV"
)
skydir = SkyCoord(266.4, -28.9, frame="icrs", unit="deg")
wcs_geom_3d = WcsGeom.create(
skydir=skydir, binsz=0.1, frame="icrs", width=(8, 4), axes=[energy_axis]
)
# create the interpolated map
m_iem_interp = m_iem_gc.interp_to_geom(
wcs_geom_3d, preserve_counts=False, method="linear", fill_value=np.nan
)
print(m_iem_interp)
WcsNDMap
geom : WcsGeom
axes : ['lon', 'lat', 'energy_true']
shape : (80, 40, 6)
ndim : 3
unit : 1 / (MeV s sr cm2)
dtype : float64
Note that preserve_counts= option should be true if the map is an
integral quantity (e.g. counts) and false if the map is a differential
quantity (e.g. intensity).
Maps operations#
Basic operators#
One can perform simple arithmetic on maps using the +, -, *,
/ operators, this works only for maps with the same geometry:
These operations can be applied between a Map and a scalar in that specific order:
iem_times_two = m_iem_10GeV * 2
# iem_times_two = 2 * m_iem_10GeV # this won't work
The logic operators can also be applied on maps (the result is a map of boolean type):
is_null = iem_minus_iem == 0
print(is_null)
WcsNDMap
geom : WcsGeom
axes : ['lon', 'lat']
shape : (80, 40)
ndim : 2
unit :
dtype : bool
Here we check that the result is True for all the well-defined
pixels (not NaN):
print(np.all(is_null.data[~np.isnan(iem_minus_iem)]))
True
Cutouts#
The WCSNDMap objects features a cutout() method, which allows
you to cut out a smaller part of a larger map. This can be useful,
e.g. when working with all-sky diffuse maps. Here is an example:
position = SkyCoord(0, 0, frame="galactic", unit="deg")
m_iem_cutout = m_iem_gc.cutout(position=position, width=(4 * u.deg, 2 * u.deg))
The returned object is again a Map object with updated WCS
information and data size. As one can see the cutout is automatically
applied to all the non-spatial axes as well. The cutout width is given
in the order of (lon, lat) and can be specified with units that will
be handled correctly.
Visualizing and Plotting#
All map objects provide a plot method for generating a visualization
of a map. This method returns figure, axes, and image objects that can
be used to further tweak/customize the image. The plot method should
be used with 2D maps, while 3D maps can be displayed with the
plot_interactive() or plot_grid() methods.
Image Plotting#
For debugging and inspecting the map data it is useful to plot or visualize the images planes contained in the map.
After reading the map we can now plot it on the screen by calling the
.plot() method:
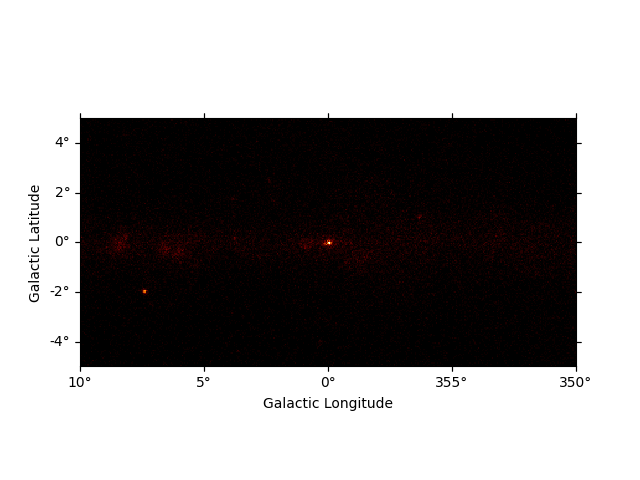
We can easily improve the plot by calling smooth() first and
providing additional arguments to plot(). Most of them are passed
further to
plt.imshow():
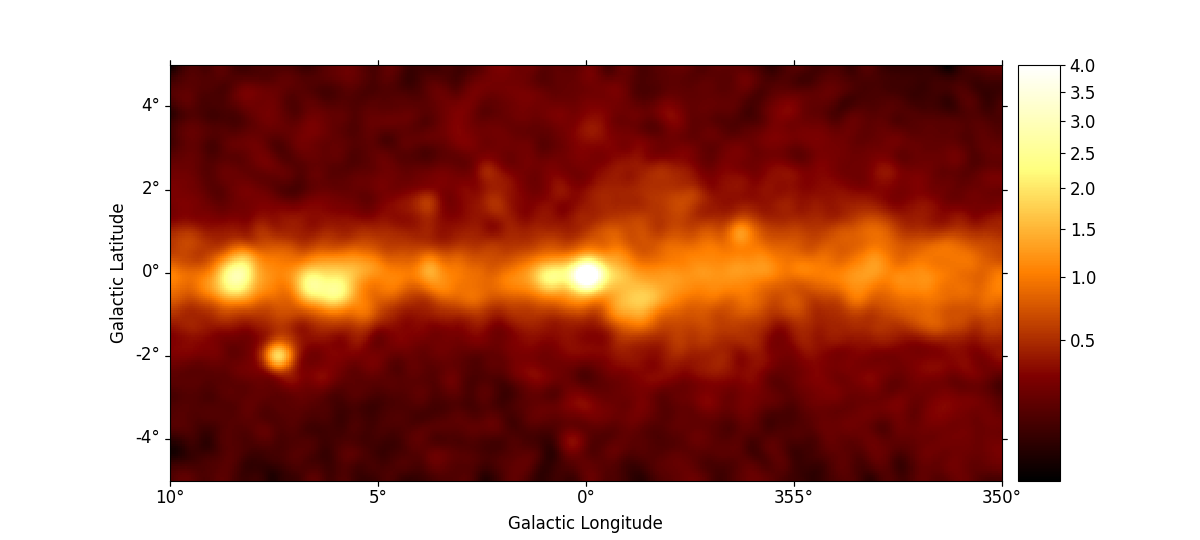
smoothed = m_3fhl_gc.smooth(width=0.2 * u.deg, kernel="gauss")
smoothed.plot(stretch="sqrt", add_cbar=True, vmax=4, cmap="inferno")
plt.show()
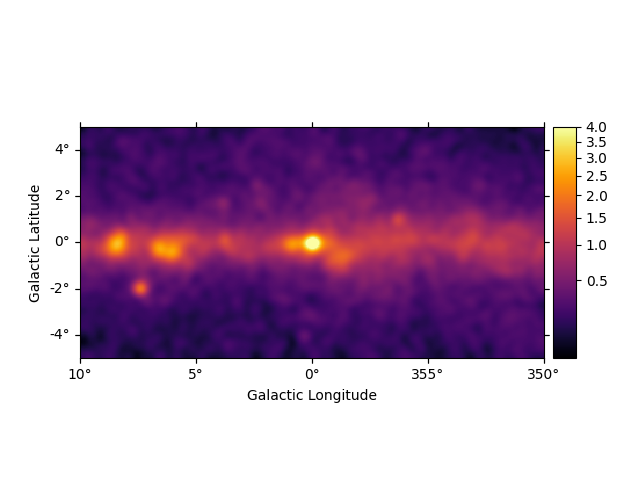
We can use the plt.rc_context() context manager to further tweak the plot by adapting the figure and font size:
rc_params = {"figure.figsize": (12, 5.4), "font.size": 12}
with plt.rc_context(rc=rc_params):
smoothed = m_3fhl_gc.smooth(width=0.2 * u.deg, kernel="gauss")
smoothed.plot(stretch="sqrt", add_cbar=True, vmax=4)
plt.show()
Cube plotting#
For maps with non-spatial dimensions the Map object features an
interactive plotting method, that works in jupyter notebooks only (Note:
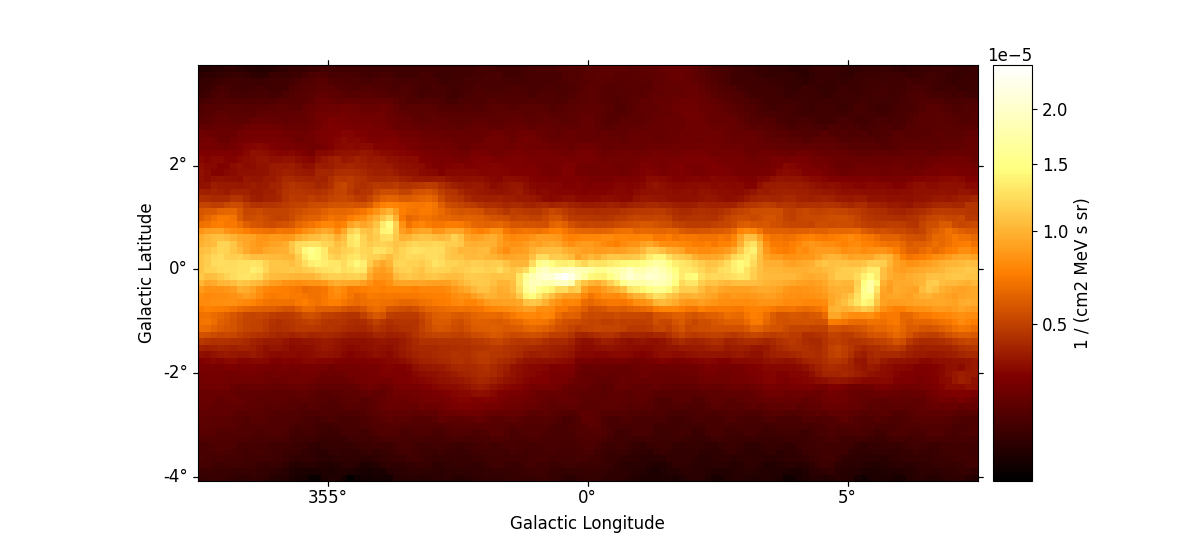
it requires the package ipywidgets to be installed). We first read a
small example cutout from the Fermi Galactic diffuse model and display
the data cube by calling plot_interactive():
rc_params = {
"figure.figsize": (12, 5.4),
"font.size": 12,
"axes.formatter.limits": (2, -2),
}
m_iem_gc.plot_interactive(add_cbar=True, stretch="sqrt", rc_params=rc_params)
plt.show()
interactive(children=(SelectionSlider(continuous_update=False, description='Select energy_true:', layout=Layout(width='50%'), options=('58.5 MeV', '80.0 MeV', '109 MeV', '150 MeV', '205 MeV', '280 MeV', '383 MeV', '523 MeV', '716 MeV', '979 MeV', '1.34 GeV', '1.83 GeV', '2.50 GeV', '3.42 GeV', '4.68 GeV', '6.41 GeV', '8.76 GeV', '12.0 GeV', '16.4 GeV', '22.4 GeV', '30.6 GeV', '41.9 GeV', '57.3 GeV', '78.4 GeV', '107 GeV', '147 GeV', '201 GeV', '274 GeV', '375 GeV', '513 GeV'), style=SliderStyle(description_width='initial'), value='58.5 MeV'), RadioButtons(description='Select stretch:', index=1, options=('linear', 'sqrt', 'log'), style=DescriptionStyle(description_width='initial'), value='sqrt'), Output()), _dom_classes=('widget-interact',))
Now you can use the interactive slider to select an energy range and the
corresponding image is displayed on the screen. You can also use the
radio buttons to select your preferred image stretching. We have passed
additional keywords using the rc_params argument to improve the
figure and font size. Those keywords are directly passed to the
plt.rc_context()
context manager.
Additionally all the slices of a 3D Map can be displayed using the
plot_grid() method. By default the colorbars bounds of the subplots
are not the same, we can make them consistent using the vmin and
vmax options:
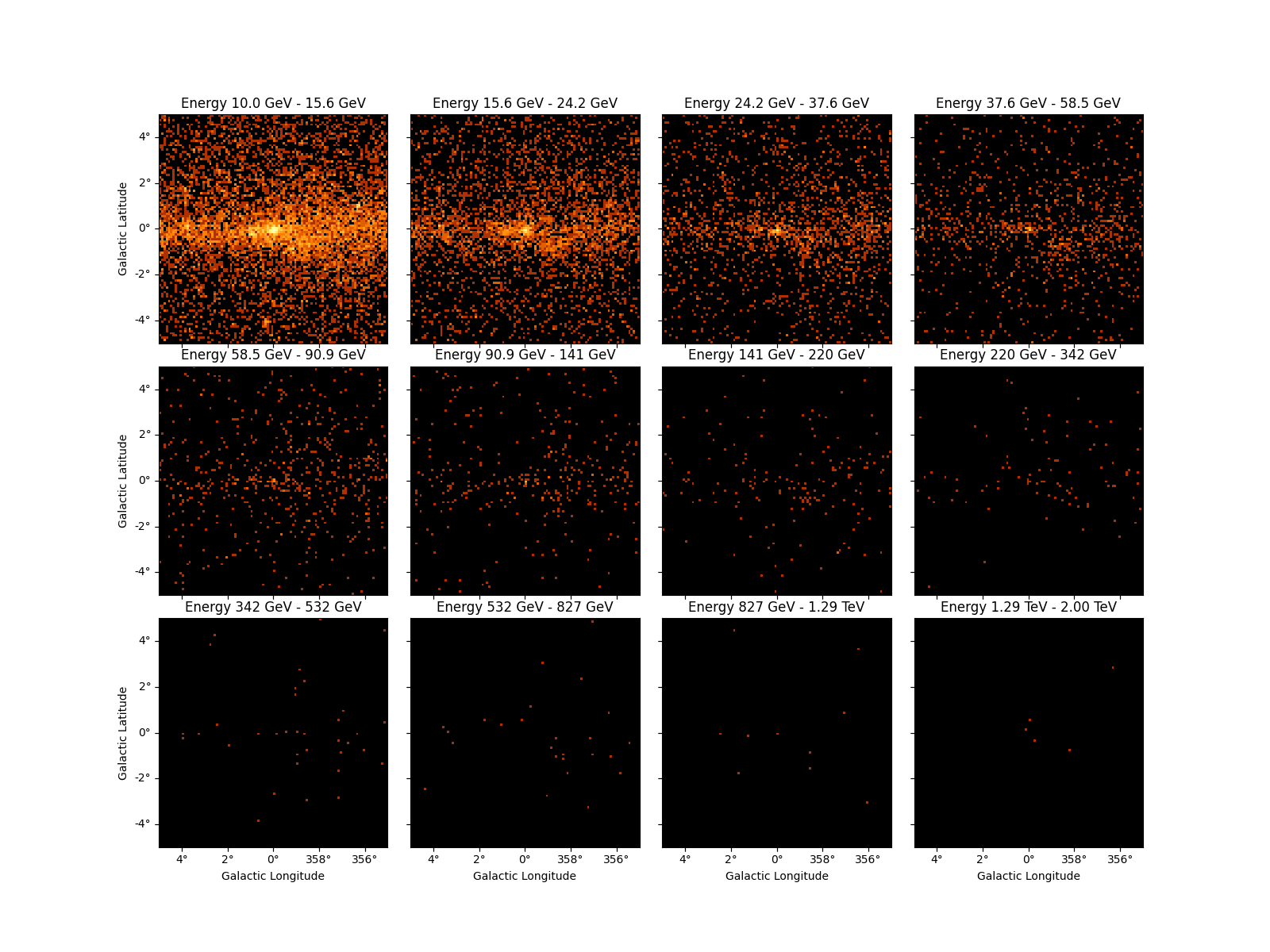
counts_3d.plot_grid(ncols=4, figsize=(16, 12), vmin=0, vmax=100, stretch="log")
plt.show()